|
|
|
Tuber magnatum |
September: The White truffle does not grow in this month.
How to reliably distinguish White Truffle from other Tuber species?

Reliable Distinguishing Characteristics of White Truffle (Tuber magnatum):
1. Morphological Features:
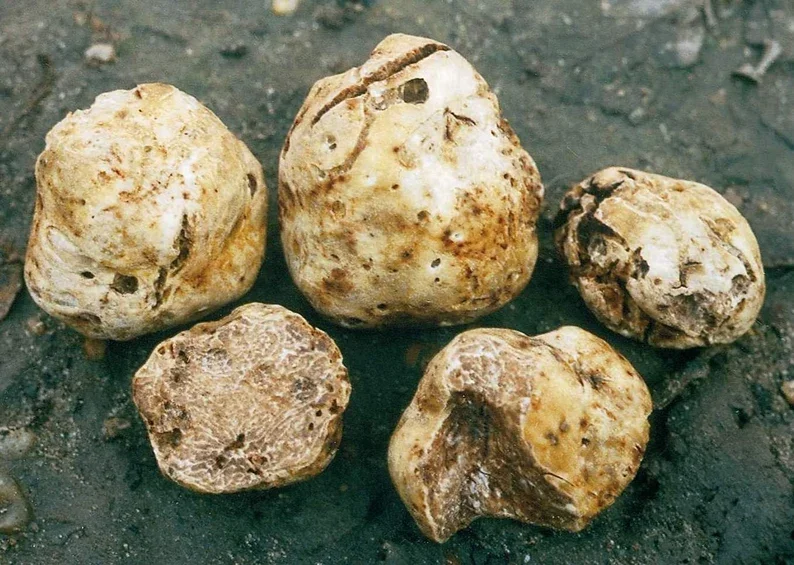
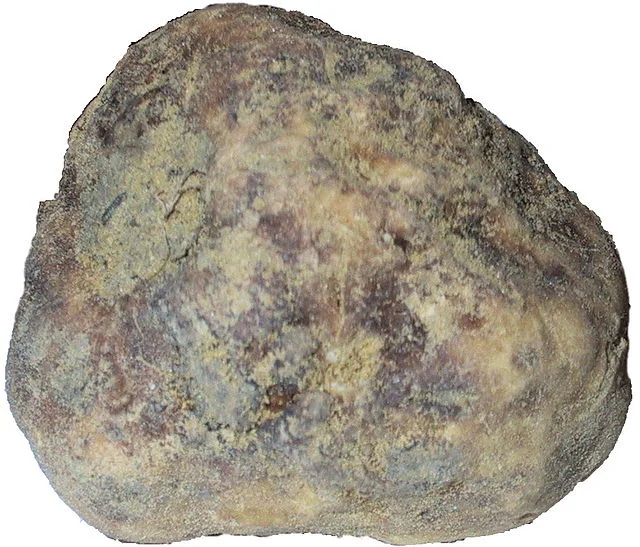
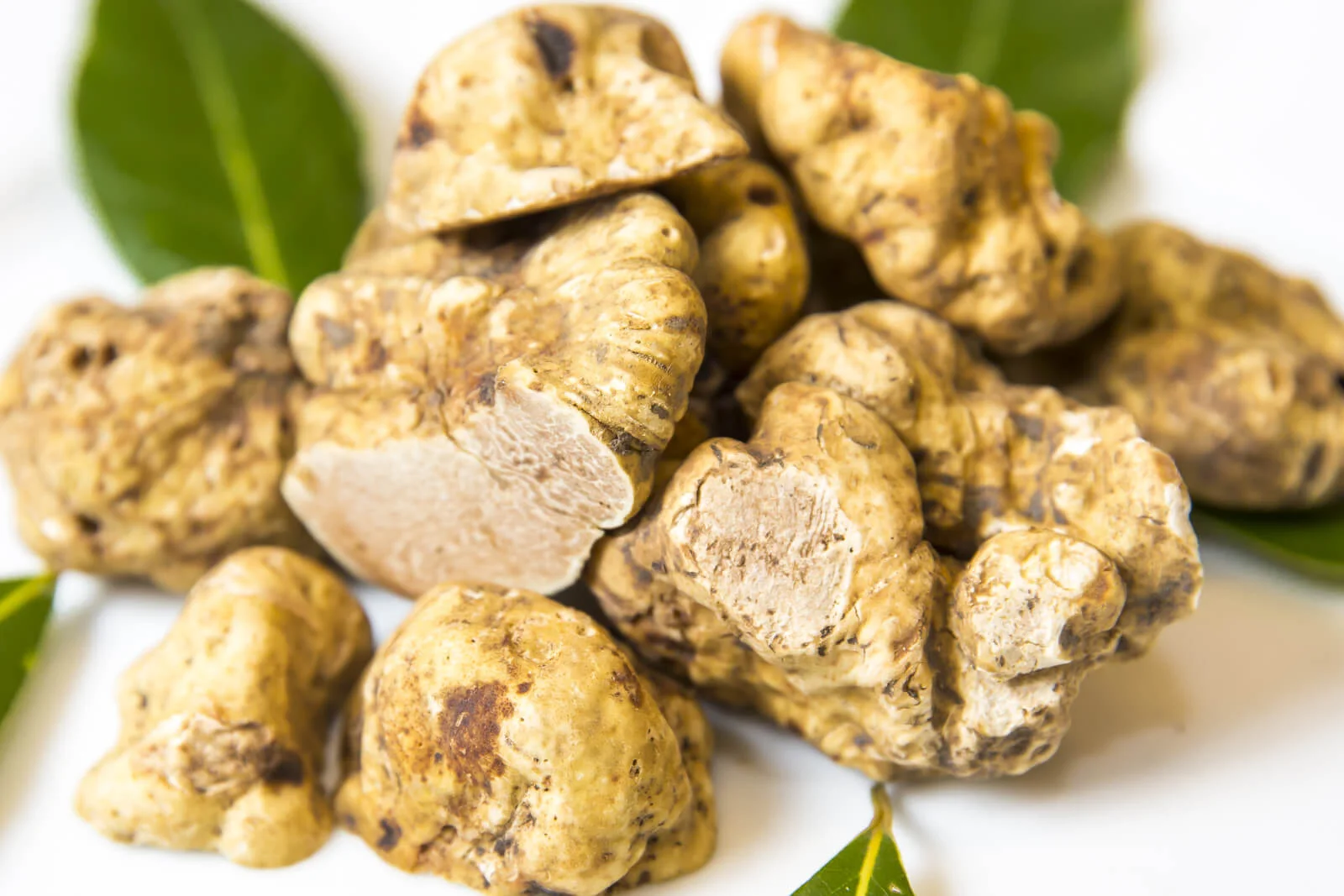
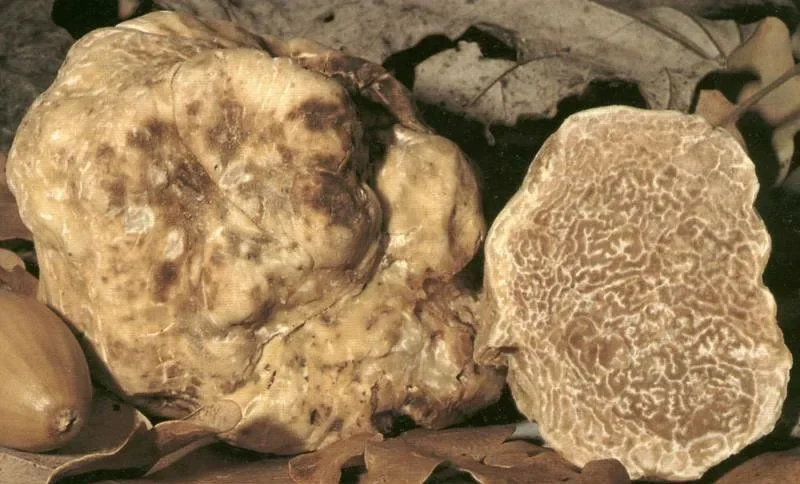
- Size and Shape: Typically small to medium - sized, with a diameter ranging between 4 - 8 cm, though larger specimens can be found. The shape is irregular or slightly rounded.
- Surface Appearance: Smooth, creamy white to light brown surface with fine, shallow reticulations that are not as pronounced as those seen on some other truffle species like Tuber aestivum.
- Peridium (Outer Skin): Thin, smooth, and delicate, often appearing wrinkled but without deep cracks.
- Pellis Coloration: Creamy white to pale ochre or yellowish - brown.
- Flesh Color: Pale ivory to light yellowish - beige when fresh, darkening slightly upon exposure to air.
2. Aromatic Profile:
- Fragrance: Intensely aromatic with a unique, earthy, garlicky, and musky scent. This characteristic fragrance is one of the most reliable indicators for distinguishing white truffles from other tuber species.
3. Microscopic Characters:
- Asci: Ovoid to ellipsoidal spore sacs containing numerous spherical spores.
- Spores: Small, round, hyaline (translucent), and typically measure around 25 - 35 μm in diameter.
- Ascospores: Numerous per ascus, usually arranged in chains within the ascus cavity.
4. Habitat and Ecology:
- Host Plants: Found predominantly in association with deciduous trees such as oak (Quercus spp.) and hazel (Corylus avellana) in well - drained, calcareous soils.
- Geographical Range: Native to northern Italy (particularly Piedmont region) and southern France.
5. Comparison with Other Species:
- Black Summer Truffle (Tuber aestivum): Has a rough, black outer skin with deeper reticulations and lacks the intense garlic - like aroma typical of Tuber magnatum.
- Burgundy Truffle (Tuber uncinatum): Often has a reddish - brown exterior and a less intense, more fruity aroma compared to the white truffle.
- Chinese Truffle (Tuber indicum): Lacks the same intensity of aroma and flavor profile, often having a milder, earthier scent.
6. Expertise and Tools:
- Truffle Dogs/Swine: Traditionally used for their acute sense of smell to locate buried truffles.
- Microscopy: Microscopic examination of spore morphology and arrangement can confirm identity.
- Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectroscopy (GC - MS): Advanced analytical techniques can identify volatile compounds specific to Tuber magnatum.
By combining these morphological, olfactory, ecological, and microscopic characteristics, you can reliably distinguish Tuber magnatum (White Truffle) from other Tuber species.
1. Morphological Features:
- Size and Shape: Typically small to medium - sized, with a diameter ranging between 4 - 8 cm, though larger specimens can be found. The shape is irregular or slightly rounded.
- Surface Appearance: Smooth, creamy white to light brown surface with fine, shallow reticulations that are not as pronounced as those seen on some other truffle species like Tuber aestivum.
- Peridium (Outer Skin): Thin, smooth, and delicate, often appearing wrinkled but without deep cracks.
- Pellis Coloration: Creamy white to pale ochre or yellowish - brown.
- Flesh Color: Pale ivory to light yellowish - beige when fresh, darkening slightly upon exposure to air.
2. Aromatic Profile:
- Fragrance: Intensely aromatic with a unique, earthy, garlicky, and musky scent. This characteristic fragrance is one of the most reliable indicators for distinguishing white truffles from other tuber species.
3. Microscopic Characters:
- Asci: Ovoid to ellipsoidal spore sacs containing numerous spherical spores.
- Spores: Small, round, hyaline (translucent), and typically measure around 25 - 35 μm in diameter.
- Ascospores: Numerous per ascus, usually arranged in chains within the ascus cavity.
4. Habitat and Ecology:
- Host Plants: Found predominantly in association with deciduous trees such as oak (Quercus spp.) and hazel (Corylus avellana) in well - drained, calcareous soils.
- Geographical Range: Native to northern Italy (particularly Piedmont region) and southern France.
5. Comparison with Other Species:
- Black Summer Truffle (Tuber aestivum): Has a rough, black outer skin with deeper reticulations and lacks the intense garlic - like aroma typical of Tuber magnatum.
- Burgundy Truffle (Tuber uncinatum): Often has a reddish - brown exterior and a less intense, more fruity aroma compared to the white truffle.
- Chinese Truffle (Tuber indicum): Lacks the same intensity of aroma and flavor profile, often having a milder, earthier scent.
6. Expertise and Tools:
- Truffle Dogs/Swine: Traditionally used for their acute sense of smell to locate buried truffles.
- Microscopy: Microscopic examination of spore morphology and arrangement can confirm identity.
- Gas Chromatography - Mass Spectroscopy (GC - MS): Advanced analytical techniques can identify volatile compounds specific to Tuber magnatum.
By combining these morphological, olfactory, ecological, and microscopic characteristics, you can reliably distinguish Tuber magnatum (White Truffle) from other Tuber species.
Key identification features: pale exterior, smooth surface, intense aroma

Tuber magnatum, commonly known as the white truffle or Alba truffle, is a highly prized edible mushroom with distinct key identification features:
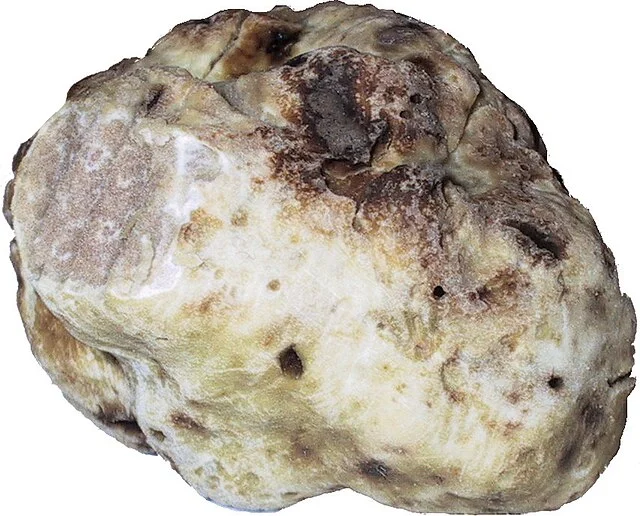
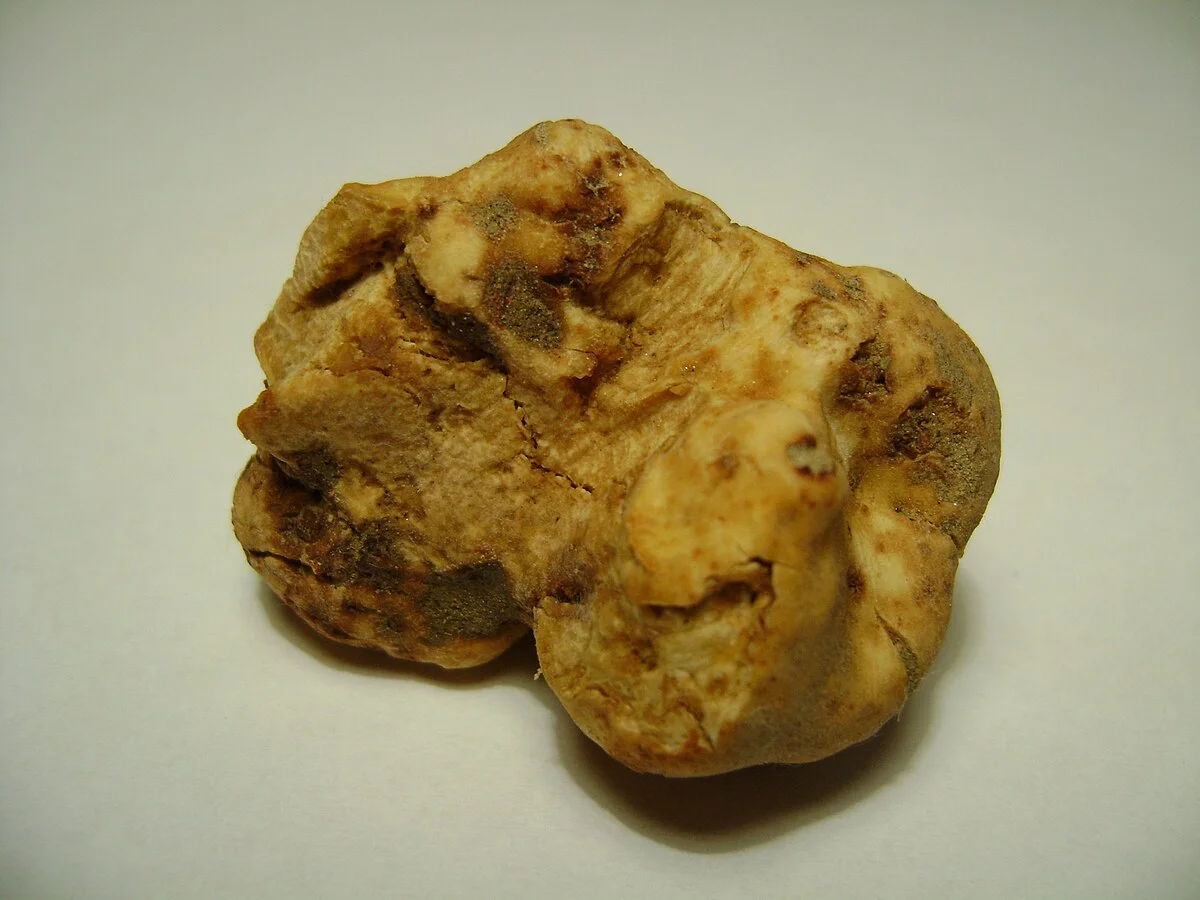
1. Exterior Color and Appearance:
- Pale to off - white or light cream - colored skin (peridium).
- Smooth or slightly wrinkled surface without prominent warts or bumps compared to other truffle species.
2. Aroma:
- Intense, earthy, garlicky, and musky scent that becomes more pronounced when the truffle is cut open.
- The aroma is often described as pungent, rich, and complex, making it one of the most sought - after culinary ingredients worldwide.
3. Shape and Size:
- Typically round or irregularly shaped.
- Medium - sized, usually ranging from golf ball size up to larger specimens depending on maturity.
4. Interior Structure:
- White to ivory interior flesh with marbled veins of black or dark brown.
- Firm texture when fresh, becoming softer as it ages.
5. Habitat and Ecology:
- Found primarily in northern Italy, particularly in the Piedmont region around Alba.
- Often associated with deciduous trees such as oak (Quercus) and hazel (Corylus avellana), where they form mycorrhizal relationships.
6. Seasonality:
- Primarily harvested during autumn and winter months (September through December).
Safety Considerations: - Ensure proper identification by an expert before consumption due to potential confusion with similar - looking but inedible or toxic truffle species.
- Purchase from reputable sources to avoid fraudulent products.
- Store properly at low temperatures (~4°C) wrapped in paper towels or damp cloths to maintain freshness and prevent mold growth.
These characteristics make Tuber magnatum easily distinguishable from other truffle species and highlight its unique qualities valued in gourmet cuisine.
1. Exterior Color and Appearance:
- Pale to off - white or light cream - colored skin (peridium).
- Smooth or slightly wrinkled surface without prominent warts or bumps compared to other truffle species.
2. Aroma:
- Intense, earthy, garlicky, and musky scent that becomes more pronounced when the truffle is cut open.
- The aroma is often described as pungent, rich, and complex, making it one of the most sought - after culinary ingredients worldwide.
3. Shape and Size:
- Typically round or irregularly shaped.
- Medium - sized, usually ranging from golf ball size up to larger specimens depending on maturity.
4. Interior Structure:
- White to ivory interior flesh with marbled veins of black or dark brown.
- Firm texture when fresh, becoming softer as it ages.
5. Habitat and Ecology:
- Found primarily in northern Italy, particularly in the Piedmont region around Alba.
- Often associated with deciduous trees such as oak (Quercus) and hazel (Corylus avellana), where they form mycorrhizal relationships.
6. Seasonality:
- Primarily harvested during autumn and winter months (September through December).
- Purchase from reputable sources to avoid fraudulent products.
- Store properly at low temperatures (~4°C) wrapped in paper towels or damp cloths to maintain freshness and prevent mold growth.
These characteristics make Tuber magnatum easily distinguishable from other truffle species and highlight its unique qualities valued in gourmet cuisine.
How to distinguish from Tuber borchii and other white truffles?

Identification of Tuber magnatum (White Alba Truffle):
To distinguish Tuber magnatum (the highly prized White Alba Truffle) from similar species like Tuber borchii, consider the following key characteristics:
1. Appearance: - Color: The outer skin (peridium) of T. marzuolo (common name for T. berchii) is typically more yellowish - brown or olive - green compared to the whitish - beige or light brown coloration of T. magnatum.
- Surface Texture: Both have a rough surface but T. burchii often has larger warts or bumps on its surface, while T. magnatum tends to be smoother with smaller granules.
2. Aroma: - T. magnatum: Known for its intensely complex aroma described as earthy, garlicky, musky, and slightly fruity. This scent is considered one of the most powerful among all truffle varieties.
- T. borchii: Has a milder, less intense aroma that may still include notes of garlic and mushrooms but lacks the same depth and complexity found in T. magnatum.
3. Size and Shape: - T. magnatum: Generally larger than T. borchii, often reaching sizes up to 8 - 12 cm in diameter. It also tends to have a rounder shape.
- T. borchii: Smaller, usually ranging between 4 - 6 cm in diameter, and can appear somewhat irregular or elongated.
4. Seasonality: - T. magnatum: Primarily harvested during autumn and winter months (October - December).
- T. borchii: More commonly available earlier in the season, starting from late summer through early fall (August - November).
5. Habitat: - T. magnatum: Found predominantly in northern Italy, particularly in Piedmont regions such as Alba.
- T. borchii: Widespread across central and southern Europe, including France, Spain, Hungary, and Croatia.
Safety Considerations: While both species are edible and safe when properly identified, it’s crucial to avoid consuming any truffle that shows signs of mold, discoloration, or an off odor. Always purchase truffles from reputable sources and ensure they are fresh before consumption.
If you’re unsure about identification, consult a mycologist or experienced truffle hunter.
To distinguish Tuber magnatum (the highly prized White Alba Truffle) from similar species like Tuber borchii, consider the following key characteristics:
- Surface Texture: Both have a rough surface but T. burchii often has larger warts or bumps on its surface, while T. magnatum tends to be smoother with smaller granules.
- T. borchii: Has a milder, less intense aroma that may still include notes of garlic and mushrooms but lacks the same depth and complexity found in T. magnatum.
- T. borchii: Smaller, usually ranging between 4 - 6 cm in diameter, and can appear somewhat irregular or elongated.
- T. borchii: More commonly available earlier in the season, starting from late summer through early fall (August - November).
- T. borchii: Widespread across central and southern Europe, including France, Spain, Hungary, and Croatia.
If you’re unsure about identification, consult a mycologist or experienced truffle hunter.
Are there poisonous mushrooms that resemble White Truffle?

Yes, there are several mushrooms that can be confused with the highly valuable and edible White Truffle (Tuber magnatum) due to their appearance or growth habits. However, it's important to note that no known mushroom species is a direct toxic look - alike of true truffles like Tuber magnatum.
The confusion usually arises from other subterranean fungi or mushrooms growing above ground that share some superficial characteristics such as size, coloration, or habitat preferences. Here are a few examples of potentially dangerous mushrooms that could cause misidentification if not properly examined:
1. False Truffles (Helvella spp., Pseudotubera spp.): These fungi may have similar underground fruiting bodies but lack the distinct aroma and texture of true truffles. Some false truffles can be bitter or indigestible.
2. Earthballs (Scleroderma spp.): Earthballs are large, round, and often brownish - black when mature. They grow underground or partially exposed and can superficially resemble immature truffles. However, they contain irritant chemicals called sclerodermatoxins which can cause gastrointestinal distress if ingested.
3. Inocybe spp. (especially species commonly found in similar habitats): While these mushrooms do not typically grow underground, they sometimes occur in similar environments where truffles might be hunted for. Many Inocybes are hallucinogenic or toxic.
4. Amanita spp. (particularly Amanitas with bulbous bases): Although Amanitas primarily produce above - ground fruiting bodies, certain species like Amanita virosa or Amanita phalloides (Death Cap) have been mistakenly associated with truffle hunting due to their bulbous base structures. When dug up accidentally during truffle searches, they can pose serious risks since many Amanitas are deadly poisonous.
Key Takeaways: - True white truffles (Tuber magnatum) don't have exact toxic counterparts.
- The primary danger comes from confusing them with other underground fungi or accidentally encountering toxic mushrooms while searching for truffles.
- Always rely on expert knowledge or consult professional mycologists before consuming any wild - gathered mushrooms, especially those harvested underground.
The confusion usually arises from other subterranean fungi or mushrooms growing above ground that share some superficial characteristics such as size, coloration, or habitat preferences. Here are a few examples of potentially dangerous mushrooms that could cause misidentification if not properly examined:
1. False Truffles (Helvella spp., Pseudotubera spp.): These fungi may have similar underground fruiting bodies but lack the distinct aroma and texture of true truffles. Some false truffles can be bitter or indigestible.
2. Earthballs (Scleroderma spp.): Earthballs are large, round, and often brownish - black when mature. They grow underground or partially exposed and can superficially resemble immature truffles. However, they contain irritant chemicals called sclerodermatoxins which can cause gastrointestinal distress if ingested.
3. Inocybe spp. (especially species commonly found in similar habitats): While these mushrooms do not typically grow underground, they sometimes occur in similar environments where truffles might be hunted for. Many Inocybes are hallucinogenic or toxic.
4. Amanita spp. (particularly Amanitas with bulbous bases): Although Amanitas primarily produce above - ground fruiting bodies, certain species like Amanita virosa or Amanita phalloides (Death Cap) have been mistakenly associated with truffle hunting due to their bulbous base structures. When dug up accidentally during truffle searches, they can pose serious risks since many Amanitas are deadly poisonous.
- The primary danger comes from confusing them with other underground fungi or accidentally encountering toxic mushrooms while searching for truffles.
- Always rely on expert knowledge or consult professional mycologists before consuming any wild - gathered mushrooms, especially those harvested underground.
What are the authentication methods for genuine White Truffles?

Authentication Methods for Genuine White Truffles (Tuber magnatum)
White truffles, particularly Tuber magnatum, are highly valued culinary delights known for their intense aroma and delicate flavor. However, due to their high market value, counterfeit products have become a concern. Here are some reliable methods used to authenticate genuine white truffles:
1. Morphological Characteristics - Shape: Typically irregular or roundish with an uneven surface.
- Color: Externally brownish - black with a rough texture internally creamy white to light yellow with marbled veins.
- Size: Usually ranges from walnut - sized to larger than a fist.
- Aroma: Intensely earthy, garlicky, and musky scent.
2. Microscopic Examination - Ascospores: Microscopic examination of spores under a microscope can reveal characteristic features such as size, shape, and color.
- Peridium Structure: The outer skin (peridium) has specific microscopic structures that vary between species.
3. Chemical Analysis - Volatile Compounds: Gas chromatography - mass spectrometry (GC - MS) is often employed to analyze volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which provide unique chemical fingerprints.
- DNA Barcoding: DNA sequencing techniques like PCR amplification and sequencing of specific gene regions (ITS region) can confirm the species identity.
4. Geographical Origin Verification - Regional Certification: Some regions, notably Alba in Piedmont, Italy, offer certifications guaranteeing authenticity based on local harvesting practices.
- Traceability Systems: Use of blockchain technology or QR codes to track the origin and supply chain of truffle products.
5. Expert Assessment - Truffle Connoisseurs: Experts trained in identifying truffle varieties through sensory evaluation (appearance, smell, taste).
- Professional Harvesters: Local farmers and professional hunters who know the regional terroir and characteristics of genuine truffles.
By combining these methods, consumers and professionals can ensure they are purchasing authentic Tuber magnatum white truffles.
White truffles, particularly Tuber magnatum, are highly valued culinary delights known for their intense aroma and delicate flavor. However, due to their high market value, counterfeit products have become a concern. Here are some reliable methods used to authenticate genuine white truffles:
- Color: Externally brownish - black with a rough texture internally creamy white to light yellow with marbled veins.
- Size: Usually ranges from walnut - sized to larger than a fist.
- Aroma: Intensely earthy, garlicky, and musky scent.
- Peridium Structure: The outer skin (peridium) has specific microscopic structures that vary between species.
- DNA Barcoding: DNA sequencing techniques like PCR amplification and sequencing of specific gene regions (ITS region) can confirm the species identity.
- Traceability Systems: Use of blockchain technology or QR codes to track the origin and supply chain of truffle products.
- Professional Harvesters: Local farmers and professional hunters who know the regional terroir and characteristics of genuine truffles.
By combining these methods, consumers and professionals can ensure they are purchasing authentic Tuber magnatum white truffles.
In which specific regions does White Truffle naturally grow?

White truffles (Tuber magnatum), also known as Alba or Piedmont white truffles, are found primarily in the following specific regions of Italy and neighboring countries:
1. Piedmont Region (Italy)
- Specifically around the towns of Alba, Asti, Monferrato, and Alessandria.
2. Lombardy Region (Italy)
- Areas such as Valtellina and Brianza.
3. Emilia - Romagna Region (Italy)
- Particularly in the provinces of Parma and Piacenza.
4. Marche Region (Italy)
- Notably in the province of Macerata.
5. Slovenia
- Primarily in the Karst Plateau region near the Italian border.
6. Croatia
- Found in Istrian Peninsula areas like Buje and Buzet.
These truffles typically thrive in deciduous forests with well - drained soils rich in calcium carbonate, often growing symbiotically with oak, poplar, and hazelnut trees. The season for hunting Tuber magnatum is generally from September to December, peaking between October and November when their aroma and flavor are at their best.
1. Piedmont Region (Italy)
- Specifically around the towns of Alba, Asti, Monferrato, and Alessandria.
2. Lombardy Region (Italy)
- Areas such as Valtellina and Brianza.
3. Emilia - Romagna Region (Italy)
- Particularly in the provinces of Parma and Piacenza.
4. Marche Region (Italy)
- Notably in the province of Macerata.
5. Slovenia
- Primarily in the Karst Plateau region near the Italian border.
6. Croatia
- Found in Istrian Peninsula areas like Buje and Buzet.
These truffles typically thrive in deciduous forests with well - drained soils rich in calcium carbonate, often growing symbiotically with oak, poplar, and hazelnut trees. The season for hunting Tuber magnatum is generally from September to December, peaking between October and November when their aroma and flavor are at their best.
When is the peak harvesting season for White Truffles?

The peak harvesting season for White Truffles (Tuber magnatum) typically occurs from October to December. However, they can sometimes be found as early as September and as late as January, depending on weather conditions and specific regions within their natural habitats such as northern Italy, particularly Piedmont and Lombardy.
How do weather conditions affect White Truffle development?

Weather conditions significantly influence the growth and development of Tuber magnatum, commonly known as the white truffle. Here are some key factors that impact its habitat and seasonality:
1. Temperature - Optimal Range: White truffles thrive within a specific temperature range, typically between 12°C to 24°C (54°F - 75°F).
- Cooler Autumn Periods: The best growing period for white truffles is during autumn when temperatures drop slightly but remain above freezing. This cool - down stimulates spore germination and mycelium formation.
- Extreme Temperatures: Prolonged periods of extreme heat or cold can negatively affect their development by either stunting growth or killing the fungi.
2. Precipitation - Moisture Balance: Adequate rainfall is crucial for white truffle development. However, excessive rain can lead to waterlogging, which may cause root rot and hinder fungal growth.
- Seasonal Rainfall Patterns: In regions like Italy's Alba district, where white truffles are abundant, seasonal rains during spring and early summer help maintain soil moisture levels necessary for truffle fruiting later in the year.
3. Humidity - High Humidity Levels: White truffles prefer humid environments with moderate humidity levels (around 60% - 80%). High humidity helps maintain soil moisture content, which is essential for fungal activity.
- Low Humidity Risks: Dry conditions can reduce soil moisture, leading to slower growth rates or even death of developing truffles.
4. Soil Conditions - Well - Drained Soil: While moisture is important, well - draining soils prevent waterlogging and ensure adequate oxygen supply to roots and mycorrhizae.
- pH and Nutrients: Weather indirectly affects soil pH and nutrient availability. Cold winters and warm springs contribute to nutrient cycling, while proper drainage ensures optimal soil chemistry for truffle production.
5. Wind and Sunlight - Moderate Wind: Mild winds help distribute spores and improve air circulation around trees hosting truffle mycorrhizae.
- Partial Shade: Excessive sunlight can dry out the soil too quickly, whereas partial shade from oak and hazelnut trees provides ideal microclimates for truffle growth.
In summary, favorable weather conditions - moderate temperatures, balanced precipitation, appropriate humidity, and suitable soil characteristics - are critical for the successful development of Tuber magnatum. White truffles require a delicate balance of these environmental factors to fruit optimally during their peak season, primarily autumn.
- Cooler Autumn Periods: The best growing period for white truffles is during autumn when temperatures drop slightly but remain above freezing. This cool - down stimulates spore germination and mycelium formation.
- Extreme Temperatures: Prolonged periods of extreme heat or cold can negatively affect their development by either stunting growth or killing the fungi.
- Seasonal Rainfall Patterns: In regions like Italy's Alba district, where white truffles are abundant, seasonal rains during spring and early summer help maintain soil moisture levels necessary for truffle fruiting later in the year.
- Low Humidity Risks: Dry conditions can reduce soil moisture, leading to slower growth rates or even death of developing truffles.
- pH and Nutrients: Weather indirectly affects soil pH and nutrient availability. Cold winters and warm springs contribute to nutrient cycling, while proper drainage ensures optimal soil chemistry for truffle production.
- Partial Shade: Excessive sunlight can dry out the soil too quickly, whereas partial shade from oak and hazelnut trees provides ideal microclimates for truffle growth.
In summary, favorable weather conditions - moderate temperatures, balanced precipitation, appropriate humidity, and suitable soil characteristics - are critical for the successful development of Tuber magnatum. White truffles require a delicate balance of these environmental factors to fruit optimally during their peak season, primarily autumn.
Optimal growing conditions: soil composition, tree associations, climate

Taxon: Tuber magnatum (White Alba Truffle)
Optimal Growing Conditions Soil Composition - Deep, well - drained soils with good aeration and water retention capacity.
- Prefer calcareous or slightly alkaline soils (pH range of 7.5 - 8.0).
- Rich in organic matter and humus content.
- Typically found on limestone or marl substrates.
Tree Associations - Primarily associated with deciduous trees such as:
- Oak (Quercus)
- Poplar (Populus)
- Willow (Salix)
- Hazelnut (Corylus avellana)
- Occasionally grows under conifers like Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) in certain regions.
Climate - Mediterranean - type climates with mild winters and hot, dry summers.
- Annual rainfall between 600 - 1,000 mm.
- Temperatures ranging from - 5°C to +40°C, but optimal growth occurs within the range of 10°C - 25°C.
- High humidity levels during the autumn months are crucial for fruiting.
These conditions create an ideal habitat for the development and fruiting of Tuber magnatum, which is typically harvested in autumn when the ground temperature reaches approximately 12°C - 15°C.
- Prefer calcareous or slightly alkaline soils (pH range of 7.5 - 8.0).
- Rich in organic matter and humus content.
- Typically found on limestone or marl substrates.
- Oak (Quercus)
- Poplar (Populus)
- Willow (Salix)
- Hazelnut (Corylus avellana)
- Occasionally grows under conifers like Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) in certain regions.
- Annual rainfall between 600 - 1,000 mm.
- Temperatures ranging from - 5°C to +40°C, but optimal growth occurs within the range of 10°C - 25°C.
- High humidity levels during the autumn months are crucial for fruiting.
These conditions create an ideal habitat for the development and fruiting of Tuber magnatum, which is typically harvested in autumn when the ground temperature reaches approximately 12°C - 15°C.
Geographical distribution and traditional growing areas

Taxon: Tuber magnatum (Piedmont White Truffle)
Geographical Distribution Piedmont white truffles, scientifically known as Tuber magnatum, are endemic to specific regions of Northern Italy, particularly the Piedmont region. Their natural geographical range is limited primarily to the following Italian regions:
- Piedmont: The Alba area (Langhe hills) is globally renowned for producing some of the highest - quality specimens.
- Lombardy: Specifically around the Valtellina valley.
- Emilia - Romagna: Particularly in the Parma province.
- Veneto: Around the Asolo area.
Additionally, smaller populations can be found in other European countries such as:
- France (especially Savoy region)
- Slovenia
- Croatia
Traditional Growing Areas The most celebrated traditional growing areas for Tuber magnatum include:
1. Langhe Hills near Alba, Piedmont: This area is considered the global epicenter for this species due to its unique soil composition, climate, and symbiotic relationship with oak trees (Quercus pubescens) and hazel trees (Corylus avellana).
- Key Locations: Acqui Terme, Asti, Monferrato, Barolo.
2. Valtellina Valley, Lombardy: Known for its high - quality truffles, this region benefits from a microclimate that supports truffle growth.
- Key Locations: Morbegno, Sondrio.
3. Parma Province, Emilia - Romagna: Famous for its culinary traditions, including prosciutto di Parma and parmigiano reggiano, where truffles have been historically harvested alongside these products.
- Key Locations: Langhirano, Soragna.
4. Asolo Area, Veneto: A lesser - known but significant producer of white truffles.
- Key Location: Asolo.
These regions share common characteristics like well - drained calcareous soils, mild winters, warm summers, and the presence of deciduous trees, which create ideal conditions for the mycorrhizal association necessary for Tuber magnatum's development.
- Piedmont: The Alba area (Langhe hills) is globally renowned for producing some of the highest - quality specimens.
- Lombardy: Specifically around the Valtellina valley.
- Emilia - Romagna: Particularly in the Parma province.
- Veneto: Around the Asolo area.
Additionally, smaller populations can be found in other European countries such as:
- France (especially Savoy region)
- Slovenia
- Croatia
1. Langhe Hills near Alba, Piedmont: This area is considered the global epicenter for this species due to its unique soil composition, climate, and symbiotic relationship with oak trees (Quercus pubescens) and hazel trees (Corylus avellana).
- Key Locations: Acqui Terme, Asti, Monferrato, Barolo.
2. Valtellina Valley, Lombardy: Known for its high - quality truffles, this region benefits from a microclimate that supports truffle growth.
- Key Locations: Morbegno, Sondrio.
3. Parma Province, Emilia - Romagna: Famous for its culinary traditions, including prosciutto di Parma and parmigiano reggiano, where truffles have been historically harvested alongside these products.
- Key Locations: Langhirano, Soragna.
4. Asolo Area, Veneto: A lesser - known but significant producer of white truffles.
- Key Location: Asolo.
These regions share common characteristics like well - drained calcareous soils, mild winters, warm summers, and the presence of deciduous trees, which create ideal conditions for the mycorrhizal association necessary for Tuber magnatum's development.
Optimal storage conditions to preserve delicate aroma

To optimally store Tuber magnatum (white truffle), the following conditions are recommended to preserve its delicate and complex aroma:
1. Temperature Control: Store at a temperature range of 0°C to +4°C. This low - temperature environment helps slow down enzymatic activity and microbial growth while maintaining the truffle's volatile compounds responsible for its intense flavor.
2. Humidity Levels: Maintain humidity levels between 85% - 95%. High humidity prevents dehydration and drying out of the truffles, which can lead to loss of moisture and subsequent degradation of their aromatic profile.
3. Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation or air circulation to prevent mold formation and allow the release of gases produced by respiration. While some gas exchange is necessary, avoid direct exposure to drafts that could cause desiccation.
4. Storage Medium: Place truffles in a container lined with absorbent paper (such as paper towels or kitchen parchment) to absorb excess moisture and odors. Regularly change the paper every few days to maintain freshness.
5. Avoid Direct Light Exposure: Keep truffles away from light sources, especially sunlight, as it can degrade the aromatic compounds over time.
6. Separate Storage: Avoid storing truffles near strong - smelling foods or products. Truffles have porous skins and can easily absorb surrounding odors, altering their natural scent.
7. Short - Term Storage Period: Ideal consumption should occur within 3 - 7 days after harvesting. Beyond this period, the intensity of the aroma begins to diminish significantly.
By adhering to these optimal storage conditions, you can effectively prolong the shelf life and preserve the exquisite aroma of Tuber magnatum.
1. Temperature Control: Store at a temperature range of 0°C to +4°C. This low - temperature environment helps slow down enzymatic activity and microbial growth while maintaining the truffle's volatile compounds responsible for its intense flavor.
2. Humidity Levels: Maintain humidity levels between 85% - 95%. High humidity prevents dehydration and drying out of the truffles, which can lead to loss of moisture and subsequent degradation of their aromatic profile.
3. Ventilation: Ensure proper ventilation or air circulation to prevent mold formation and allow the release of gases produced by respiration. While some gas exchange is necessary, avoid direct exposure to drafts that could cause desiccation.
4. Storage Medium: Place truffles in a container lined with absorbent paper (such as paper towels or kitchen parchment) to absorb excess moisture and odors. Regularly change the paper every few days to maintain freshness.
5. Avoid Direct Light Exposure: Keep truffles away from light sources, especially sunlight, as it can degrade the aromatic compounds over time.
6. Separate Storage: Avoid storing truffles near strong - smelling foods or products. Truffles have porous skins and can easily absorb surrounding odors, altering their natural scent.
7. Short - Term Storage Period: Ideal consumption should occur within 3 - 7 days after harvesting. Beyond this period, the intensity of the aroma begins to diminish significantly.
By adhering to these optimal storage conditions, you can effectively prolong the shelf life and preserve the exquisite aroma of Tuber magnatum.
How to properly clean White Truffles after harvesting?

To properly clean Tuber magnatum (White Truffle) after harvesting, follow these steps carefully to preserve their delicate aroma and quality:
1. Avoid Rinsing with Water:
Do not wash the truffles under running water as this can damage their texture and dilute their intense flavor.
2. Brush Off Dirt:
Use a soft - bristled brush or a small, dry pastry brush to gently remove any dirt or debris from the surface of the truffle. Be careful not to press too hard, which could bruise it.
3. Wipe with a Dry Cloth:
After brushing, wipe the truffle with a clean, dry cloth or paper towel to remove any remaining dust or soil particles.
4. Store Properly:
Once cleaned, store the white truffle in a ventilated container lined with a damp paper towel or a sealed glass jar with uncooked rice to absorb moisture. Keep them refrigerated at around 2 - 6°C (35 - 43°F).
By following these steps, you ensure that your freshly harvested Tuber magnatum retains its exceptional taste and aroma for longer.
1. Avoid Rinsing with Water:
Do not wash the truffles under running water as this can damage their texture and dilute their intense flavor.
2. Brush Off Dirt:
Use a soft - bristled brush or a small, dry pastry brush to gently remove any dirt or debris from the surface of the truffle. Be careful not to press too hard, which could bruise it.
3. Wipe with a Dry Cloth:
After brushing, wipe the truffle with a clean, dry cloth or paper towel to remove any remaining dust or soil particles.
4. Store Properly:
Once cleaned, store the white truffle in a ventilated container lined with a damp paper towel or a sealed glass jar with uncooked rice to absorb moisture. Keep them refrigerated at around 2 - 6°C (35 - 43°F).
By following these steps, you ensure that your freshly harvested Tuber magnatum retains its exceptional taste and aroma for longer.
Best methods for short-term preservation of fresh truffles

1. Refrigeration with Rice or Paper Towels
- Place the truffle(s) in an airtight container lined with dry rice or paper towels.
- The rice absorbs moisture while maintaining humidity levels suitable for preserving the truffle's aroma and texture.
- Store at temperatures between 4 - 6°C (39 - 43°F).
2. Vacuum Packaging
- Vacuum - seal the truffle in food - grade plastic bags.
- This method minimizes exposure to air and helps retain the truffle’s volatile compounds, extending its shelf life by up to one week when stored refrigerated.
3. Humidity Controlled Chambers
- Use specialized chambers that control both temperature and humidity.
- Ideally, these should maintain relative humidity around 85 - 90% and temperatures close to 4°C (39°F).
4. Wrapped in Moistened Cheesecloth or Paper Towel
- Wrap the truffle loosely in slightly damp cheesecloth or paper towel to prevent drying out but avoid direct contact with water.
- Refrigerate immediately after wrapping.
5. Freezing (for Longer Term)
- While freezing is not recommended for short - term preservation due to potential loss of aroma, it may be considered if immediate consumption is not possible.
- Freeze whole or grated truffles in vacuum - sealed containers or freezer bags. Thaw slowly in the refrigerator before use.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that Tuber magnatum retains its exceptional taste and fragrance for as long as possible during short - term storage.
How to prevent aroma loss during storage?

To prevent the loss of aroma and maintain quality when storing Tuber magnatum (white truffles), consider these best practices for processing and storage:
1. Controlled Humidity - Store white truffles at a relative humidity level between 85% - 95%. This prevents dehydration while avoiding mold growth.
2. Temperature Control - Ideal temperature range is 0°C to +4°C. Cold temperatures slow down enzyme activity and microbial growth but should not be below freezing as it can damage the delicate cells.
3. Proper Packaging - Use perforated paper or cloth bags, which allow air circulation without drying out the truffle. Aluminum foil or plastic containers are unsuitable because they trap moisture and promote spoilage.
4. Avoid Direct Contact with Other Foods - Truffles absorb odors from other foods. If stored improperly, their unique aroma may diminish or become tainted by neighboring items.
5. Regular Monitoring - Check truffles daily for signs of mold or deterioration. Discard any that show visible signs of decay to avoid contaminating others.
6. Short - Term Storage - White truffles have a relatively short shelf life. For optimal flavor retention, consume them within 3 - 7 days after harvesting.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce aroma loss and preserve the exquisite flavors of Tuber magnatum during storage.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly reduce aroma loss and preserve the exquisite flavors of Tuber magnatum during storage.
Shelf life and signs of White Truffle spoilage

- Factors affecting shelf life: Temperature, humidity, packaging method, and handling practices.
- Avoid freezing as it can damage the aroma and texture.
2. Humidity: High humidity levels around 85% - 95% are recommended to prevent drying out.
3. Packaging: Store truffles wrapped in paper towels or unbleached parchment paper that absorbs moisture.
- Re - wrap daily with fresh paper to absorb any excess moisture.
- Alternatively, store them in a sealed container lined with damp paper towel but avoid direct contact with water.
4. Avoid light exposure: Keep in a dark place away from sunlight.
- Surface discoloration: Brownish spots or patches on the surface.
- Texture changes: Softening, mushiness, or slime formation.
2. Odor:
- Loss of intense earthy, garlicky, and musky aroma.
- Development of unpleasant odors such as ammonia - like smells or sourness.
3. Weight loss:
- Noticeable weight reduction due to dehydration and drying out.
4. Mold growth:
- Visible mold appearing on the outer skin or inside cracks.
If any of these signs appear, it's best to discard the truffle immediately to avoid potential health risks.
How to properly prepare White Truffles for cooking?

- The scent should be strong and pleasant, reminiscent of garlic, mushrooms, and soil.
- Avoid truffles that smell sour or musty.
- Do not wash the truffle under running water as it may dilute its fragrance.
- Place the container in the refrigerator next to eggs or other foods that will absorb the truffle's aroma.
- Use within 2 - 3 days for optimal freshness.
- Grating: Grate the truffle coarsely over dishes just before serving.
- Infusing: Slice the truffle into small pieces and infuse them in olive oil or butter by letting them steep together at room temperature for several hours or overnight.
- Cooking with Infusions: Add truffle - infused oils or butters to sauces, soups, or roasted vegetables.
- Baking: Incorporate finely chopped truffle into doughs for pastries or breads.
By following these steps, you'll ensure that your white truffles retain their rich flavors and enhance the overall dining experience.
Best culinary applications to maximize delicate flavor

Taxon: Tuber magnatum (White Alba Truffle)
Best Culinary Applications to Maximize Delicate Flavor 1. Raw and Shaved over Rich Dishes
- Application: White truffles are best enjoyed raw due to their intense aroma and delicate flavor. Shaving them thinly with a truffle shaver or microplane ensures that the flavor is released without being overwhelmed by cooking.
- Examples:
- Over fresh pasta dishes like tagliolini or pappardelle with butter or light cream sauce.
- On risotto Milanese or risotto alla bianca.
- As a garnish for steak tartare or carpaccio.
2. Lightly Cooked Eggs
- Application: The earthy, garlicky notes of white truffles pair beautifully with eggs, especially when cooked gently to retain their delicate texture.
- Examples:
- Poached eggs on toast or brioche with truffle shavings.
- Soft - boiled eggs served with toast points and truffle oil.
- Truffled scrambled eggs made with heavy cream.
3. Simple Vegetable Preparations
- Application: Mild vegetables enhance rather than compete with the truffle’s complex flavors.
- Examples:
- Roasted potatoes or parsnips finished with truffle shavings.
- Blanched asparagus or green beans dressed with olive oil and truffle flakes.
- Grilled mushrooms (like porcini or chanterelles) paired with shaved truffle.
4. Rich Meats and Seafood
- Application: Truffles elevate rich proteins by adding depth and complexity.
- Examples:
- Seared foie gras slices topped with shaved truffle.
- Carpaccio di manzo (raw beef carpaccio) with Parmesan cheese and truffle.
- Caviar or osetra roe combined with shaved truffle for an opulent brunch dish.
5. Sauces and Dressings
- Application: While whole truffles should not be boiled or simmered, their essence can be captured through infused oils or reduced stocks.
- Examples:
- Truffle - infused olive oil drizzled over salads or grilled meats.
- Whipped mascarpone or crème fraîche mixed with truffle paste as a dip or spread.
- Light vinaigrette dressings enhanced with truffle essence.
6. Desserts and Sweet Pairings
- Application: Surprisingly, truffles also work well in desserts, particularly those featuring chocolate or nuts.
- Examples:
- Chocolate mousse or ganache garnished with finely chopped truffle.
- Hazelnut praline or nut brittle with truffle shavings.
- Baked apples or poached pears finished with a touch of truffle.
Key Tips for Maximizing Flavor - Store truffles properly wrapped in paper towels lined with rice or breadcrumbs to maintain moisture and prevent odor transfer.
- Serve truffles at room temperature to fully release their aromatic compounds.
- Avoid overcooking or prolonged exposure to heat, which can diminish their nuanced flavors.
- Application: White truffles are best enjoyed raw due to their intense aroma and delicate flavor. Shaving them thinly with a truffle shaver or microplane ensures that the flavor is released without being overwhelmed by cooking.
- Examples:
- Over fresh pasta dishes like tagliolini or pappardelle with butter or light cream sauce.
- On risotto Milanese or risotto alla bianca.
- As a garnish for steak tartare or carpaccio.
2. Lightly Cooked Eggs
- Application: The earthy, garlicky notes of white truffles pair beautifully with eggs, especially when cooked gently to retain their delicate texture.
- Examples:
- Poached eggs on toast or brioche with truffle shavings.
- Soft - boiled eggs served with toast points and truffle oil.
- Truffled scrambled eggs made with heavy cream.
3. Simple Vegetable Preparations
- Application: Mild vegetables enhance rather than compete with the truffle’s complex flavors.
- Examples:
- Roasted potatoes or parsnips finished with truffle shavings.
- Blanched asparagus or green beans dressed with olive oil and truffle flakes.
- Grilled mushrooms (like porcini or chanterelles) paired with shaved truffle.
4. Rich Meats and Seafood
- Application: Truffles elevate rich proteins by adding depth and complexity.
- Examples:
- Seared foie gras slices topped with shaved truffle.
- Carpaccio di manzo (raw beef carpaccio) with Parmesan cheese and truffle.
- Caviar or osetra roe combined with shaved truffle for an opulent brunch dish.
5. Sauces and Dressings
- Application: While whole truffles should not be boiled or simmered, their essence can be captured through infused oils or reduced stocks.
- Examples:
- Truffle - infused olive oil drizzled over salads or grilled meats.
- Whipped mascarpone or crème fraîche mixed with truffle paste as a dip or spread.
- Light vinaigrette dressings enhanced with truffle essence.
6. Desserts and Sweet Pairings
- Application: Surprisingly, truffles also work well in desserts, particularly those featuring chocolate or nuts.
- Examples:
- Chocolate mousse or ganache garnished with finely chopped truffle.
- Hazelnut praline or nut brittle with truffle shavings.
- Baked apples or poached pears finished with a touch of truffle.
- Serve truffles at room temperature to fully release their aromatic compounds.
- Avoid overcooking or prolonged exposure to heat, which can diminish their nuanced flavors.
How to use truffle slicers for perfect shavings?

- Ensure you have a high - quality truffle slicer or mandoline designed specifically for delicate foods like truffles.
- Clean and dry all utensils before starting.
2. Selecting the Right Truffle
- Choose a fresh, firm Tuber magnatum. With its intense aroma and rich flavor, this variety is ideal for showcasing in dishes.
- Look for a truffle that feels heavy for its size and has an earthy, musky scent.
3. Preparing the Truffle
- Wipe any dirt off the surface of the truffle gently with a damp cloth or soft brush.
- Do not wash it under running water as this can dilute its flavor.
4. Using the Truffle Slicer
- Position your truffle on the slicer’s base, ensuring it is stable and secure.
- Adjust the slicer's blade thickness according to your preference. Thinner slices are typically used for garnishing, while thicker ones work well for sauces or pasta dishes.
5. Slicing Technique
- Hold the truffle firmly but gently against the slicer.
- Apply even pressure as you guide the truffle through the blade, creating uniform slices.
- Rotate the truffle slightly between cuts to maximize yield and ensure even slicing.
6. Storing Unused Portions
- Store unused portions of the truffle in a sealed container lined with paper towels or rice to absorb moisture.
- Keep refrigerated until ready to use again.
7. Serving Tips
- For optimal presentation, arrange thinly sliced truffle over warm dishes such as risotto, pasta, eggs, or steak.
- Allow the heat from the dish to release the truffle's aroma and enhance its flavor.
By following these steps, you'll be able to showcase the exquisite flavors and aromas of Tuber magnatum, elevating your culinary creations to new heights.
Classic Italian recipes featuring White Truffles

Arborio rice, chicken stock, butter, olive oil, shallots, dry white wine, freshly grated Parmesan cheese, salt, pepper, and fresh white truffle.
- Preparation:
Cook the rice in broth until al dente, then finish with butter and Parmesan. Grate fresh white truffle on top just before serving.
Fresh tagliolini pasta, unsalted butter, fresh sage leaves, salt, black pepper, freshly grated white truffle.
- Preparation:
Boil pasta in salted water. Drizzle melted butter over cooked pasta, toss with fresh sage leaves, season with salt and pepper, and finish by grating white truffle over each portion.
Fresh eggs, heavy cream, unsalted butter, salt, pepper, freshly grated white truffle.
- Preparation:
Whisk eggs and cream together. Over medium heat, cook gently while stirring constantly. Add butter at the end, season, and garnish with freshly grated white truffle.
Thinly sliced raw beef tenderloin, arugula, extra virgin olive oil, lemon juice, sea salt, freshly ground black pepper, finely grated white truffle.
- Preparation:
Arrange thin slices of beef on a plate. Top with arugula, drizzle with olive oil and lemon juice, season with salt and pepper, and finish with freshly grated white truffle.
Homemade fettuccine, heavy cream, unsalted butter, freshly grated Pecorino Romano cheese, salt, pepper, freshly grated white truffle.
- Preparation:
Cook pasta in boiling water. Drain and return to pot. Add warm cream and butter, toss well. Season generously with Pecorino Romano and finish with freshly grated white truffle.
These recipes showcase how white truffles can elevate simple yet elegant dishes, adding an unparalleled depth of flavor.
Pairing suggestions with different foods and wines

Truffle Pairings for Tuber Magnatum (White Alba Truffle):
Food Pairings: - Pasta: White truffles are traditionally shaved over fresh pasta dishes like tagliatelle or pappardelle with butter or light cream sauces.
- Eggs: Poached eggs, scrambled eggs, omelets, or deviled eggs enhanced by the aroma of white truffle.
- Risotto: A classic pairing where the richness of risotto complements the delicate flavor of the truffle.
- Meats: Lighter meats such as veal, chicken, or turkey can be paired with truffle to enhance their natural flavors without overwhelming them.
- Seafood: Scallops, lobster, or crab can benefit from a subtle touch of truffle shavings.
- Mashed Potatoes: Add a luxurious element to mashed potatoes by incorporating some grated truffle.
- Bread & Butter: Simple yet elegant - truffle butter spread on warm bread is an indulgent treat.
- Salads: Salad greens dressed with olive oil and finished with truffle shavings create a unique twist.
Wine Pairings: - Sparkling Wines: Prosecco or Champagne pair well due to their effervescence and ability to cleanse the palate between bites.
- Light Red Wines: Nebbiolo - based wines like Barolo or Barbaresco complement the earthy notes of the truffle while maintaining balance.
- Dry White Wines: Pinot Grigio or Chardonnay work well, especially if the dish has lighter elements.
- Fortified Wines: Sweet dessert wines like Vin Santo or Moscato d'Asti provide a contrasting sweetness that enhances the umami - rich flavors of the truffle.
These pairings highlight the versatility and elegance of Tuber magnatum, showcasing its distinct aromas and enhancing culinary experiences.
- Eggs: Poached eggs, scrambled eggs, omelets, or deviled eggs enhanced by the aroma of white truffle.
- Risotto: A classic pairing where the richness of risotto complements the delicate flavor of the truffle.
- Meats: Lighter meats such as veal, chicken, or turkey can be paired with truffle to enhance their natural flavors without overwhelming them.
- Seafood: Scallops, lobster, or crab can benefit from a subtle touch of truffle shavings.
- Mashed Potatoes: Add a luxurious element to mashed potatoes by incorporating some grated truffle.
- Bread & Butter: Simple yet elegant - truffle butter spread on warm bread is an indulgent treat.
- Salads: Salad greens dressed with olive oil and finished with truffle shavings create a unique twist.
- Light Red Wines: Nebbiolo - based wines like Barolo or Barbaresco complement the earthy notes of the truffle while maintaining balance.
- Dry White Wines: Pinot Grigio or Chardonnay work well, especially if the dish has lighter elements.
- Fortified Wines: Sweet dessert wines like Vin Santo or Moscato d'Asti provide a contrasting sweetness that enhances the umami - rich flavors of the truffle.
These pairings highlight the versatility and elegance of Tuber magnatum, showcasing its distinct aromas and enhancing culinary experiences.
Is cultivation of White Truffle possible in artificial conditions?

Cultivation of the white truffle (Tuber magnatum) under fully artificial conditions is challenging and not yet consistently successful compared to its natural growth environment. However, significant progress has been made in recent years through various techniques aimed at simulating natural conditions for truffle production.
Current Methods for White Truffle Cultivation 1. Inoculation of Host Trees
The most common method involves planting host trees (such as oak or hazelnut) that have been inoculated with Tuber magnatum spores. This technique requires specific soil types, climate conditions, and careful management but can yield results after several years.
2. Controlled Environment Greenhouses
Some researchers are experimenting with greenhouse - based systems where environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, and light levels are closely controlled. While promising, this approach remains experimental and expensive.
3. Artificial Mycorrhization Systems
Advanced techniques involve creating artificial mycorrhizal associations between truffle spores and tree roots outside their natural habitat. These methods aim to mimic natural symbiotic relationships under laboratory conditions.
4. Soil Amelioration Techniques
Adjustments to soil composition, pH, and nutrient content can enhance the likelihood of successful truffle development. Even so, these efforts often require extensive trial - and - error and may still depend on favorable climatic conditions.
Challenges in Artificial Cultivation - Complex Symbiosis: White truffles rely heavily on a mutualistic relationship with certain tree species, making it difficult to replicate this interaction artificially.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and soil quality must be precisely managed, which is complex and costly.
- Long Maturation Periods: White truffles typically take 7 - 15 years to mature, requiring long - term commitment from growers.
- High Failure Rates: Despite advancements, many attempts at artificial cultivation fail due to insufficient understanding of all factors influencing truffle fruiting.
Conclusion While full - scale commercial cultivation of Tuber magnatum under completely artificial conditions remains elusive, partial success has been achieved using semi - natural approaches like inoculation and controlled environments. Further research and technological innovations could eventually make large - scale artificial cultivation feasible.
The most common method involves planting host trees (such as oak or hazelnut) that have been inoculated with Tuber magnatum spores. This technique requires specific soil types, climate conditions, and careful management but can yield results after several years.
2. Controlled Environment Greenhouses
Some researchers are experimenting with greenhouse - based systems where environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, and light levels are closely controlled. While promising, this approach remains experimental and expensive.
3. Artificial Mycorrhization Systems
Advanced techniques involve creating artificial mycorrhizal associations between truffle spores and tree roots outside their natural habitat. These methods aim to mimic natural symbiotic relationships under laboratory conditions.
4. Soil Amelioration Techniques
Adjustments to soil composition, pH, and nutrient content can enhance the likelihood of successful truffle development. Even so, these efforts often require extensive trial - and - error and may still depend on favorable climatic conditions.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature fluctuations, humidity levels, and soil quality must be precisely managed, which is complex and costly.
- Long Maturation Periods: White truffles typically take 7 - 15 years to mature, requiring long - term commitment from growers.
- High Failure Rates: Despite advancements, many attempts at artificial cultivation fail due to insufficient understanding of all factors influencing truffle fruiting.
Specific challenges in White Truffle cultivation

1. Mycorrhizal Symbiosis:
White truffles form a mutualistic relationship with certain tree species, primarily oak (Quercus), poplar (Populus), and hazelnut (Corylus avellana). The successful establishment of this symbiotic relationship is critical for truffle fruiting. This process requires precise conditions regarding soil type, pH levels, moisture content, and temperature fluctuations.
2. Soil Conditions:
Tuber magnatum thrives in well - drained calcareous soils with high alkalinity (pH between 7.5 - 8.5). Additionally, the soil must have good aeration and drainage, which can be difficult to achieve consistently across different regions or climates.
3. Climate Requirements:
White truffles require specific climate conditions that mimic those found in their native habitats - northern Italy's Piedmont region. This includes mild winters, warm summers, and moderate rainfall. Any deviation from these conditions can negatively impact truffle development.
4. Long Maturation Periods:
Unlike many agricultural crops, white truffles take years to mature - typically around 7 - 10 years after planting host trees. This long gestation period poses significant financial risks for growers who may not see returns on investment until decades later.
5. Pest and Disease Management:
Truffle plantations are susceptible to various fungal diseases and insect pests. For instance, nematodes, slugs, and other soil - borne pathogens can severely damage truffle production. Effective pest management strategies are essential but often challenging to implement without compromising the natural ecosystem.
6. Environmental Factors:
Climate change, drought, floods, and extreme weather events pose additional threats to truffle cultivation. These factors can disrupt the delicate balance required for truffle growth, leading to reduced yields or even complete crop failure.
7. Limited Scientific Understanding:
Despite extensive research, much about the life cycle and optimal growing conditions of Tuber magnatum remains unknown. Improved understanding through scientific studies could significantly enhance cultivation success rates.
8. High Initial Investment Costs:
Establishing a truffle plantation involves substantial upfront costs, including purchasing specialized spore - inoculated seedlings, preparing suitable soil, and implementing irrigation systems. These expenses make it financially risky for small - scale farmers.
9. Harvesting Difficulties:
Harvesting white truffles typically relies on trained dogs or pigs to locate the underground fruits. This method is labor - intensive and requires skilled personnel, adding another layer of complexity to the farming process.
In conclusion, while the potential rewards of successfully cultivating white truffles are immense, the process itself is fraught with numerous technical, environmental, and economic challenges. Overcoming these obstacles requires careful planning, advanced knowledge, and considerable patience.
Modern techniques in White Truffle farming

- Benefits:
- Enhances the establishment of a stable mycorrhizal association.
- Accelerates the development of truffle fruiting bodies.
- Improves nutrient uptake by the host plant.
- Ensuring well - drained soils with optimal pH levels (7 - 8).
- Incorporating organic matter to enhance soil structure and microbial activity.
- Irrigation Systems:
- Drip irrigation systems for precise water management.
- Moisture sensors to monitor soil conditions.
- Protects young trees from extreme weather conditions.
- Maintains ideal temperature and humidity ranges for truffle growth.
- Geothermal Heating:
- Used in colder regions to maintain suitable ground temperatures year - round.
- Training pigs or dogs to locate naturally occurring truffle spores.
- Reintroducing these spores into cultivated areas.
- Microbial Bioaugmentation:
- Adding beneficial microbes to promote soil health and truffle production.
- Utilizing GPS technology to map and track truffle - producing zones within fields.
- Optimizing fertilization and irrigation based on real - time data.
- Remote Monitoring Systems:
- IoT devices for continuous monitoring of environmental parameters such as temperature, moisture, and CO₂ levels.
- Introducing multiple tree species to create diverse ecosystems conducive to truffle growth.
- Wildlife Habitat Creation:
- Encouraging natural predators to control pests and diseases.
These modern techniques aim to increase the predictability and yield of white truffle harvests while maintaining ecological sustainability. By combining traditional knowledge with cutting - edge technologies, farmers can now cultivate this rare and valuable fungus more effectively than ever before.
What tree species are best for White Truffle orchards?

For successful cultivation of White Truffles (Tuber magnatum), the following tree species have proven to be most effective as host trees due to their compatibility with truffle mycorrhizae and ability to provide optimal environmental conditions:
1. Oak (Quercus spp.)
- Particularly Quercus pubescens (Downy Oak), Quercus cerris (Turkish Oak), and Quercus robur (English Oak).
2. Hornbeam (Carpinus betulus)
- Known for its resilience and adaptability to various soil types.
3. Poplar (Populus spp.)
- Populus alba (White Poplar) is often used because it grows quickly and provides suitable root systems for truffle symbiosis.
4. Chestnut (Castanea sativa)
- While less common than oaks, chestnuts can also support white truffle growth under certain conditions.
5. Ash (Fraxinus excelsior)
- This species can complement oak plantations by adding diversity and enhancing ecosystem health.
Key Considerations for Orchard Establishment: - Soil Type: Well - drained calcareous soils with pH levels between 7.5 - 8.0 are ideal.
- Climate: Mediterranean - type climates with mild winters and warm summers are preferred.
- Irrigation: Regular watering during dry periods is essential for young sapling establishment.
- Shading: Moderate shade from trees helps maintain humidity and temperature within the soil layer where truffles grow.
By selecting these compatible tree species and ensuring proper site preparation and management practices, you can increase your chances of successfully cultivating high - quality White Truffles.
1. Oak (Quercus spp.)
- Particularly Quercus pubescens (Downy Oak), Quercus cerris (Turkish Oak), and Quercus robur (English Oak).
2. Hornbeam (Carpinus betulus)
- Known for its resilience and adaptability to various soil types.
3. Poplar (Populus spp.)
- Populus alba (White Poplar) is often used because it grows quickly and provides suitable root systems for truffle symbiosis.
4. Chestnut (Castanea sativa)
- While less common than oaks, chestnuts can also support white truffle growth under certain conditions.
5. Ash (Fraxinus excelsior)
- This species can complement oak plantations by adding diversity and enhancing ecosystem health.
- Climate: Mediterranean - type climates with mild winters and warm summers are preferred.
- Irrigation: Regular watering during dry periods is essential for young sapling establishment.
- Shading: Moderate shade from trees helps maintain humidity and temperature within the soil layer where truffles grow.
By selecting these compatible tree species and ensuring proper site preparation and management practices, you can increase your chances of successfully cultivating high - quality White Truffles.
Time required from planting to first harvest

Taxon Tuber magnatum, commonly known as the white truffle or Alba truffle, is a highly prized edible mushroom that grows symbiotically with certain tree species such as oak (Quercus), hazel (Corylus avellana), and poplar (Populus).
The time required for Tuber magnatum to develop from planting (i.e., introducing mycorrhizal inoculum into soil near host trees) until the first harvest can vary significantly depending on several factors including climate, soil conditions, and the specific method of cultivation. Generally:
- Under optimal conditions, it takes approximately 7 - 10 years before the first significant harvests are possible.
- Some commercial operations may report smaller yields starting around 5 - 6 years, but these are often not economically viable.
White truffles have a slow growth cycle due to their complex ecological requirements and dependence on specific environmental conditions.
The time required for Tuber magnatum to develop from planting (i.e., introducing mycorrhizal inoculum into soil near host trees) until the first harvest can vary significantly depending on several factors including climate, soil conditions, and the specific method of cultivation. Generally:
- Under optimal conditions, it takes approximately 7 - 10 years before the first significant harvests are possible.
- Some commercial operations may report smaller yields starting around 5 - 6 years, but these are often not economically viable.
White truffles have a slow growth cycle due to their complex ecological requirements and dependence on specific environmental conditions.
How to identify and avoid counterfeit White Truffles?

To identify and avoid counterfeit White Truffle (Tuber magnatum) effectively, it's essential to understand the key characteristics of genuine truffles and be aware of common fraudulent practices used by unscrupulous sellers. Here are some detailed steps and tips for ensuring you purchase authentic white truffles:
1. Verify the Source - Trusted suppliers: Purchase from reputable dealers or directly from regions known for producing high - quality white truffles such as Alba (Piedmont), Italy.
- Seasonality: Authentic white truffles are harvested between September and December. Ensure you're buying them during this period.
2. Use Your Senses Authentic white truffles have distinct sensory qualities that can help differentiate them from imitations:
- Aroma: The scent is intensely earthy, garlicky, and musky. It should fill a room when opened.
- Texture: The skin is smooth with small bumps, not wrinkled or rough. Inside, it has marbled veins of black and white.
- Color: The exterior is pale brownish - tan, while the interior ranges from creamy white to light ivory.
3. Check Physical Appearance Counterfeits often lack these specific features:
- Size and shape: Counterfeit truffles may look too uniform or perfect in size and shape compared to natural irregularities found in real ones.
- Weight: Real truffles feel heavy for their size due to their dense flesh.
4. Be Wary of Low Prices - Price comparison: White truffles are among the most expensive foods globally. If an offer seems too good to be true, it likely is.
- Market price tracking: Stay informed about current market prices through reliable sources like specialized websites or local farmers' markets.
5. Ask for Documentation Reputable suppliers will provide documentation verifying the origin and authenticity of their products:
- Certificates of authenticity: Some suppliers issue certificates confirming the genuineness of their truffles.
- Regional stamps: In Italy, official seals or stamps indicating the region of harvest might be present on packaging.
6. Avoid Online Risks When purchasing online:
- Avoid generic e - commerce platforms: Stick to dedicated gourmet food websites or those specializing in truffles.
- Check reviews: Look at customer feedback and ratings before making a purchase.
7. Seek Expert Advice If unsure, consult experts or professional chefs who regularly work with truffles. They can help verify authenticity based on experience and knowledge.
By following these guidelines, you'll significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to counterfeit white truffles and ensure you enjoy the genuine culinary delight they represent.
- Seasonality: Authentic white truffles are harvested between September and December. Ensure you're buying them during this period.
- Aroma: The scent is intensely earthy, garlicky, and musky. It should fill a room when opened.
- Texture: The skin is smooth with small bumps, not wrinkled or rough. Inside, it has marbled veins of black and white.
- Color: The exterior is pale brownish - tan, while the interior ranges from creamy white to light ivory.
- Size and shape: Counterfeit truffles may look too uniform or perfect in size and shape compared to natural irregularities found in real ones.
- Weight: Real truffles feel heavy for their size due to their dense flesh.
- Market price tracking: Stay informed about current market prices through reliable sources like specialized websites or local farmers' markets.
- Certificates of authenticity: Some suppliers issue certificates confirming the genuineness of their truffles.
- Regional stamps: In Italy, official seals or stamps indicating the region of harvest might be present on packaging.
- Avoid generic e - commerce platforms: Stick to dedicated gourmet food websites or those specializing in truffles.
- Check reviews: Look at customer feedback and ratings before making a purchase.
By following these guidelines, you'll significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to counterfeit white truffles and ensure you enjoy the genuine culinary delight they represent.
Investment potential in truffle cultivation

- Market Value: Prices can reach up to €15,000 - €40,000 per kilogram depending on seasonality, quality, and demand.
- Health Benefits: Emerging research highlights potential health benefits such as antioxidant properties, further boosting consumer interest.
- Rarity: Wild truffles are rare and highly sought after, creating scarcity that drives prices higher.
- Yield Predictability: With proper management, yields can be more predictable compared to wild harvesting.
- Long - term Returns: Initial investment costs may be high but can yield significant returns over time, typically within 7 - 10 years post - inoculation.
- Climate Sensitivity: Truffle growth requires specific climatic conditions (moderate temperatures, well - drained soil), limiting suitable regions.
- Pest Management: Pests and diseases can significantly impact crop success rates if not managed properly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Strict regulations regarding land use, conservation, and product labeling must be adhered to.
- Focus on regions with favorable climates (Mediterranean - like conditions).
- Ensure proximity to markets or access to reliable logistics networks.
2. Partnerships and Expertise:
- Collaborate with experienced truffle growers or researchers.
- Leverage local knowledge about optimal species selection and site preparation.
3. Diversification Strategy:
- Combine truffle plantations with other agricultural activities (e.g., olive groves, vineyards) to spread risk.
4. Marketing and Branding:
- Develop strong branding and direct - to - consumer sales channels.
- Target luxury food markets and establish partnerships with high - end chefs/restaurants.
5. Sustainable Practices:
- Adopt eco - friendly farming methods to enhance brand reputation and meet growing consumer preferences for sustainability.
What factors determine the market price of White Truffles?

The market price of white truffles (Tuber magnatum), often considered one of the most valuable culinary delicacies globally, is influenced by several key factors:
1. Rarity and Limited Supply - White truffles are rare and grow wild only in specific regions such as northern Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, and parts of France. Their limited availability drives up prices significantly.
2. Harvest Seasonality - The peak season for white truffle harvesting runs from September to December. During this period, demand spikes while supply remains constrained, leading to higher prices.
3. Quality and Size - Larger and more fragrant truffles command much higher prices compared to smaller or less aromatic ones. Quality is assessed based on appearance, scent intensity, texture, and firmness.
4. Regional Origin - Truffles from renowned regions like Alba (Piedmont, Italy) fetch premium prices due to their superior quality and historical reputation.
5. Market Demand - High - end restaurants and gourmet food enthusiasts drive significant demand for white truffles, especially during special occasions like Christmas and New Year's Eve.
6. Globalization and Export - With globalized markets, high demand from international buyers - particularly in Asia, North America, and Europe - increases competition and pushes prices upward.
7. Labor Intensity and Harvest Methods - Harvesting involves skilled labor using trained dogs or pigs, which adds to production costs. Additionally, the delicate nature of handling these perishable goods requires specialized logistics and storage conditions.
8. Speculation and Market Dynamics - Like other luxury goods, speculation can influence prices. Investors may buy large quantities to sell later at a profit, affecting short - term pricing trends.
In summary, the unique combination of rarity, seasonal fluctuations, regional exclusivity, labor - intensive harvest methods, and strong global demand makes white truffles one of the world's most expensive foods.
In summary, the unique combination of rarity, seasonal fluctuations, regional exclusivity, labor - intensive harvest methods, and strong global demand makes white truffles one of the world's most expensive foods.
Why are White Truffles the most expensive mushrooms?

- White truffles (Tuber magnatum) grow wild only in specific regions such as northern Italy and parts of Croatia. Their habitat is highly specialized, requiring particular soil conditions, climate, and symbiotic relationships with tree roots. This limited geographical range restricts their availability.
2. Harvesting Difficulty
- Harvesting white truffles requires skilled labor and trained animals like dogs or pigs to locate them underground. The process is time - consuming and labor - intensive, further driving up costs.
3. Seasonality
- White truffles have a short harvest season, typically from September to December. This seasonal scarcity increases demand during these months, leading to higher prices.
4. Culinary Status Symbol
- White truffles are considered a luxury ingredient in high - end cuisine. They are often associated with Michelin - starred restaurants and gourmet dining experiences, making them a status symbol among food connoisseurs.
5. Unique Flavor Profile
- The intense aroma and unique flavor of white truffles make them highly sought after by chefs and gourmands. Their earthy, pungent scent enhances the taste of dishes, adding value to culinary creations.
6. Market Dynamics and Auctions
- Due to their exclusivity, white truffles are frequently sold at auctions where bidding can drive prices sky - high. These auctions attract wealthy buyers willing to pay premium prices for exceptional specimens.
7. Preservation Challenges
- White truffles do not keep well once harvested, losing their potency quickly. This perishability necessitates immediate consumption, which adds logistical complexity and cost.
8. Historical and Cultural Significance
- Historically, white truffles were prized by royalty and aristocracy in Europe. This legacy continues today, reinforcing their reputation as an elite food item.
Nutritional and medicinal properties

Tuber magnatum, commonly known as the white truffle or Alba truffle, is renowned not only for its exquisite culinary value but also for its nutritional and potential medicinal benefits.
Nutritional Properties - Macronutrients: White truffles are low in calories, carbohydrates, and fat, making them a relatively light food option. They contain small amounts of protein.
- Micronutrients: They are rich in vitamins (B1, B2, C), minerals (potassium, iron, zinc), and antioxidants such as polyphenols.
- Fats: The fats present are primarily unsaturated fatty acids, which can be beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation.
Medicinal Properties - Antioxidant Activity: Polyphenolic compounds found in Tuber magnatum exhibit strong antioxidant activity, potentially helping to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
- Anti - inflammatory Effects: Some studies suggest that components in white truffles may have anti - inflammatory properties, which could contribute to overall health by reducing chronic inflammation.
- Immunomodulatory Potential: Certain bioactive compounds might enhance immune function, although more research is needed to confirm this effect.
- Cardiovascular Health: Due to their content of healthy fats and antioxidants, they may support cardiovascular health by improving lipid profiles and reducing cholesterol levels.
The combination of these nutritional and possible therapeutic effects contributes significantly to the high economic value attributed to Tuber magnatum.
- Micronutrients: They are rich in vitamins (B1, B2, C), minerals (potassium, iron, zinc), and antioxidants such as polyphenols.
- Fats: The fats present are primarily unsaturated fatty acids, which can be beneficial for heart health when consumed in moderation.
- Anti - inflammatory Effects: Some studies suggest that components in white truffles may have anti - inflammatory properties, which could contribute to overall health by reducing chronic inflammation.
- Immunomodulatory Potential: Certain bioactive compounds might enhance immune function, although more research is needed to confirm this effect.
- Cardiovascular Health: Due to their content of healthy fats and antioxidants, they may support cardiovascular health by improving lipid profiles and reducing cholesterol levels.
The combination of these nutritional and possible therapeutic effects contributes significantly to the high economic value attributed to Tuber magnatum.
How to use trained dogs for truffle hunting?

To effectively utilize trained dogs for truffle hunting (specifically Tuber magnatum, the white Alba truffle), follow these steps and considerations:
1. Choose the Right Breed - Breeds commonly used include Lagotto Romagnolo, German Shepherd, Labrador Retriever, and Spaniels due to their keen sense of smell and trainability.
2. Training Process - Early Start: Begin training puppies from a young age when they are most receptive to learning.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use treats, praise, and play as rewards to encourage desired behavior.
- Gradual Exposure: Introduce the scent of truffles gradually by hiding small pieces under shallow layers of soil or leaves.
- Repetition: Consistently repeat exercises daily until the dog associates the scent with a reward.
3. Field Training - Controlled Environment: Initially hunt in controlled environments where truffles have been planted at known locations.
- Expand Difficulty: Gradually increase the complexity by introducing natural habitats with varying terrain and scents.
4. Hunting Techniques - Leash Control: Keep the dog on a leash initially to maintain control during early hunts.
- Release for Independence: Once confident, allow the dog more freedom to roam and search independently.
- Marking Behavior: Teach the dog specific behaviors (e.g., sitting or pawing) to indicate the presence of truffles.
5. Seasonal Considerations - Timing: Hunt during the peak season, typically autumn through winter, when truffles are ripe and emit strong odors.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid extremely wet or dry conditions that can affect the scent.
6. Post - Hunt Care - Reward System: Always reward the dog after successful finds to reinforce positive behavior.
- Health Monitoring: Ensure the dog stays hydrated and is protected from ticks and other potential hazards in the field.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively harness the exceptional olfactory abilities of trained dogs to locate valuable Tuber magnatum truffles efficiently and sustainably.
- Positive Reinforcement: Use treats, praise, and play as rewards to encourage desired behavior.
- Gradual Exposure: Introduce the scent of truffles gradually by hiding small pieces under shallow layers of soil or leaves.
- Repetition: Consistently repeat exercises daily until the dog associates the scent with a reward.
- Expand Difficulty: Gradually increase the complexity by introducing natural habitats with varying terrain and scents.
- Release for Independence: Once confident, allow the dog more freedom to roam and search independently.
- Marking Behavior: Teach the dog specific behaviors (e.g., sitting or pawing) to indicate the presence of truffles.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid extremely wet or dry conditions that can affect the scent.
- Health Monitoring: Ensure the dog stays hydrated and is protected from ticks and other potential hazards in the field.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively harness the exceptional olfactory abilities of trained dogs to locate valuable Tuber magnatum truffles efficiently and sustainably.
Traditional methods for locating White Truffles underground

Traditional methods for locating white truffles (Tuber magnatum) underground have been passed down through generations and rely on the keen senses of animals or trained individuals. Here are some key traditional approaches:
1. Use of Dogs
- Historically, dogs were trained to sniff out the strong aroma of mature truffle tubers buried beneath the soil. These dogs are often bred from specific breeds known for their exceptional sense of smell, such as Labrador Retrievers or German Shepherds.
- The dog is taught to signal when it detects a truffle by sitting or scratching at the ground.
2. Use of Pigs
- In many regions, particularly Italy, pigs were traditionally used because they naturally love the scent and taste of truffles. Their strong olfactory abilities make them excellent detectors.
- However, pigs can be difficult to control once they find a truffle, often eating the valuable fungus before it can be harvested. Therefore, this method has largely been replaced by using dogs.
3. Manual Searching with Tools
- Experienced truffle hunters use small spades or specialized tools called "trifoletti" to carefully dig around likely areas where truffles might grow.
- They look for signs such as swollen roots of host trees (typically oak, poplar, or hazelnut), changes in soil color, or slight bulges in the earth's surface that indicate the presence of an underground truffle.
4. Knowledge of Habitat and Seasonality
- Expert truffle hunters rely heavily on knowledge about the habitat preferences of white truffles. They search in areas with well - drained soils rich in calcium carbonate, typically under deciduous trees like oaks.
- Timing is crucial - white truffles are primarily found during autumn and winter months (October to December).
5. Truffle Hounds' Assistance
- Modern - day truffle hunting still relies on trained hounds who are specifically raised and conditioned to locate truffles. These dogs undergo rigorous training programs to develop their ability to identify the unique scent of truffles.
These traditional techniques remain effective today, especially in regions famous for their truffle production such as Alba in Piedmont, Italy.
1. Use of Dogs
- Historically, dogs were trained to sniff out the strong aroma of mature truffle tubers buried beneath the soil. These dogs are often bred from specific breeds known for their exceptional sense of smell, such as Labrador Retrievers or German Shepherds.
- The dog is taught to signal when it detects a truffle by sitting or scratching at the ground.
2. Use of Pigs
- In many regions, particularly Italy, pigs were traditionally used because they naturally love the scent and taste of truffles. Their strong olfactory abilities make them excellent detectors.
- However, pigs can be difficult to control once they find a truffle, often eating the valuable fungus before it can be harvested. Therefore, this method has largely been replaced by using dogs.
3. Manual Searching with Tools
- Experienced truffle hunters use small spades or specialized tools called "trifoletti" to carefully dig around likely areas where truffles might grow.
- They look for signs such as swollen roots of host trees (typically oak, poplar, or hazelnut), changes in soil color, or slight bulges in the earth's surface that indicate the presence of an underground truffle.
4. Knowledge of Habitat and Seasonality
- Expert truffle hunters rely heavily on knowledge about the habitat preferences of white truffles. They search in areas with well - drained soils rich in calcium carbonate, typically under deciduous trees like oaks.
- Timing is crucial - white truffles are primarily found during autumn and winter months (October to December).
5. Truffle Hounds' Assistance
- Modern - day truffle hunting still relies on trained hounds who are specifically raised and conditioned to locate truffles. These dogs undergo rigorous training programs to develop their ability to identify the unique scent of truffles.
These traditional techniques remain effective today, especially in regions famous for their truffle production such as Alba in Piedmont, Italy.
Proper techniques for harvesting without damaging the mycelium

Proper Techniques for Harvesting Tuber magnatum (White Truffle) Without Damaging Mycelium
1. Manual Digging with Care:
Use a small, narrow trowel or specialized truffle fork to gently dig around the suspected location of the truffle. Avoid using machinery that could damage the delicate mycelial network beneath the soil.
2. Minimal Soil Disturbance:
Minimize disruption to the surrounding soil and roots by carefully removing only enough earth necessary to expose the truffle. Gently loosen the soil around the truffle before lifting it out.
3. Preservation of Roots:
Be cautious not to disturb or cut tree roots during harvesting, as these are essential for the mycorrhizal relationship between the truffle fungus and host trees.
4. Marking Locations:
Mark harvested areas with stakes or flags to avoid re - digging in the same spot next season, allowing time for regeneration of the mycelium.
5. Post - Harvest Handling:
Handle freshly dug truffles with care, avoiding direct contact with metal surfaces which can cause oxidation and reduce quality. Store them in ventilated containers lined with damp paper towels or perforated plastic bags at low temperatures (~4°C).
6. Rotation and Sustainability:
Rotate harvesting sites within the truffle grove each year to prevent overexploitation and ensure long - term sustainability of the ecosystem.
By adhering to these methods, you can effectively harvest white truffles while preserving their natural habitat and ensuring future yields.
1. Manual Digging with Care:
Use a small, narrow trowel or specialized truffle fork to gently dig around the suspected location of the truffle. Avoid using machinery that could damage the delicate mycelial network beneath the soil.
2. Minimal Soil Disturbance:
Minimize disruption to the surrounding soil and roots by carefully removing only enough earth necessary to expose the truffle. Gently loosen the soil around the truffle before lifting it out.
3. Preservation of Roots:
Be cautious not to disturb or cut tree roots during harvesting, as these are essential for the mycorrhizal relationship between the truffle fungus and host trees.
4. Marking Locations:
Mark harvested areas with stakes or flags to avoid re - digging in the same spot next season, allowing time for regeneration of the mycelium.
5. Post - Harvest Handling:
Handle freshly dug truffles with care, avoiding direct contact with metal surfaces which can cause oxidation and reduce quality. Store them in ventilated containers lined with damp paper towels or perforated plastic bags at low temperatures (~4°C).
6. Rotation and Sustainability:
Rotate harvesting sites within the truffle grove each year to prevent overexploitation and ensure long - term sustainability of the ecosystem.
By adhering to these methods, you can effectively harvest white truffles while preserving their natural habitat and ensuring future yields.
Special tools and equipment for White Truffle harvesting

1. Truffle Dogs or Pigs
- Traditionally, pigs were used due to their acute sense of smell. However, dogs are now more commonly employed as they cause less damage to the soil and roots.
2. Sniffing Dog Training Gear
- Obedience collars, leashes, treats, and training aids are necessary for effective dog handling during hunting.
3. Digging Tools
- Small Hand Shovels: Lightweight and small enough to carefully dig around the truffle without damaging it.
- Trowels: For precision work when uncovering smaller truffles.
- Forks: Used gently to loosen soil around the truffle.
4. Protective Gloves
- To handle truffles with care and prevent contamination from dirt or oils on hands.
5. Storage Containers
- Airtight containers lined with moist paper towels to maintain humidity and freshness post - harvest.
6. Field Notebook and GPS Device
- For recording locations where truffles are found, which helps track future growth patterns.
7. Kneeling Pad or Mat
- Provides comfort while working close to the ground.
8. First Aid Kit
- Essential for any outdoor activity involving animals and manual labor.
9. Water Bottles and Snacks
- Important for maintaining energy levels during long hours spent searching.
By using these tools and following proper techniques, you can maximize your chances of successfully harvesting high - quality white truffles while preserving the ecosystem for future yields.
How to determine the perfect ripeness for harvesting?

To determine the perfect ripeness of Tuber magnatum (white truffle), consider these key indicators and steps:
1. Size - Ideal size is typically between 4 - 8 cm in diameter. Large truffles are generally more mature but should not be overly large as they can become overripe or hollow inside.
2. Weight - A dense and heavy truffle indicates good quality and maturity. Lightweight truffles may indicate dryness or poor development.
3. Surface Appearance - The skin should have a smooth texture with small bumps and ridges. Overly wrinkled or cracked surfaces might suggest that the truffle has started to degrade.
- Color should range from light brown to dark brown with creamy white marbling visible when cut open.
4. Aroma - One of the most critical factors. A perfectly ripe white truffle will emit a strong, earthy, garlicky, and slightly fruity aroma. If the scent is weak or absent, it’s likely underdeveloped. Conversely, an overly pungent odor could mean it's past its prime.
5. Texture - Cutting into the truffle reveals its internal structure. It should be firm yet yielding, with a uniform, fine - grained interior. Avoid mushy or spongy textures, which signify spoilage.
6. Harvest Season - White truffles usually reach peak ripeness during autumn (October - December) in regions like Piedmont, Italy. Timely harvesting within this period ensures optimal flavor and aroma.
By combining these observations - size, weight, appearance, aroma, texture, and seasonality - a harvester can accurately assess whether a Tuber magnatum is at its prime for picking.
- Color should range from light brown to dark brown with creamy white marbling visible when cut open.
By combining these observations - size, weight, appearance, aroma, texture, and seasonality - a harvester can accurately assess whether a Tuber magnatum is at its prime for picking.
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Aland Islands
Aland Islands Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria American Samoa
American Samoa Andorra
Andorra Angola
Angola Anguilla
Anguilla Antarctica
Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Aruba
Aruba Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bahamas
Bahamas Bahrain
Bahrain Bangladesh
Bangladesh Barbados
Barbados Belarus
Belarus Belgium
Belgium Belize
Belize Benin
Benin Bermuda
Bermuda Bhutan
Bhutan Bolivia
Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana
Botswana Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island Brazil
Brazil British Virgin Islands
British Virgin Islands Brunei
Brunei Bulgaria
Bulgaria Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Burundi
Burundi Cambodia
Cambodia Cameroon
Cameroon Canada
Canada Cape Verde
Cape Verde Caribbean Netherlands
Caribbean Netherlands Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Chagos
Chagos Chile
Chile China
China Christmas Island
Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Cook Islands
Cook Islands Costa Rica
Costa Rica Croatia
Croatia Cuba
Cuba Curaçao
Curaçao Cyprus
Cyprus Czechia
Czechia DR Congo
DR Congo Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea Denmark
Denmark Djibouti
Djibouti Dominica
Dominica Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt El Salvador
El Salvador Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Eritrea
Eritrea Estonia
Estonia Eswatini
Eswatini Ethiopia
Ethiopia Falkland Islands
Falkland Islands Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands Fiji
Fiji Finland
Finland France
France French Guiana
French Guiana French Polynesia
French Polynesia French Southern and Antarctic Lands
French Southern and Antarctic Lands Gabon
Gabon Gambia
Gambia Georgia
Georgia Germany
Germany Ghana
Ghana Gibraltar
Gibraltar Greece
Greece Greenland
Greenland Grenada
Grenada Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe Guam
Guam Guatemala
Guatemala Guernsey
Guernsey Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Guyana
Guyana Haiti
Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands
Heard Island and McDonald Islands Honduras
Honduras Hong Kong
Hong Kong Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Ireland
Ireland Isle of Man
Isle of Man Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast Jamaica
Jamaica Japan
Japan Jersey
Jersey Jordan
Jordan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kenya
Kenya Kiribati
Kiribati Kosovo
Kosovo Kuwait
Kuwait Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Laos
Laos Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Lesotho
Lesotho Liberia
Liberia Libya
Libya Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Macau
Macau Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Malta
Malta Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands Martinique
Martinique Mauritania
Mauritania Mauritius
Mauritius Mayotte
Mayotte Mexico
Mexico Micronesia
Micronesia Moldova
Moldova Monaco
Monaco Mongolia
Mongolia Montenegro
Montenegro Montserrat
Montserrat Morocco
Morocco Mozambique
Mozambique Myanmar
Myanmar Namibia
Namibia Nauru
Nauru Nepal
Nepal Netherlands
Netherlands Netherlands Antilles
Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia
New Caledonia New Zealand
New Zealand Nicaragua
Nicaragua Niger
Niger Nigeria
Nigeria Niue
Niue Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island North Macedonia
North Macedonia Northern Mariana Islands
Northern Mariana Islands Norway
Norway Oman
Oman Pakistan
Pakistan Palau
Palau Palestine
Palestine Panama
Panama Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Philippines
Philippines Pitcairn Islands
Pitcairn Islands Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico Qatar
Qatar Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Romania
Romania Russia
Russia Rwanda
Rwanda Réunion
Réunion Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Martin
Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa
Samoa San Marino
San Marino Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Senegal
Senegal Serbia
Serbia Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro Seychelles
Seychelles Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Singapore
Singapore Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Somalia
Somalia South Africa
South Africa South Georgia
South Georgia South Korea
South Korea South Sudan
South Sudan Spain
Spain Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Sudan
Sudan Suriname
Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen
Svalbard and Jan Mayen Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Syria
Syria São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe Taiwan
Taiwan Tajikistan
Tajikistan Tanzania
Tanzania Thailand
Thailand Timor-Leste
Timor-Leste Togo
Togo Tokelau
Tokelau Tonga
Tonga Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu
Tuvalu Uganda
Uganda Ukraine
Ukraine United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States United States Minor Outlying Islands
United States Minor Outlying Islands United States Virgin Islands
United States Virgin Islands Uruguay
Uruguay Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan Vanuatu
Vanuatu Vatican City
Vatican City Venezuela
Venezuela Vietnam
Vietnam Wallis and Futuna
Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara
Western Sahara Yemen
Yemen Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe