|
|
|
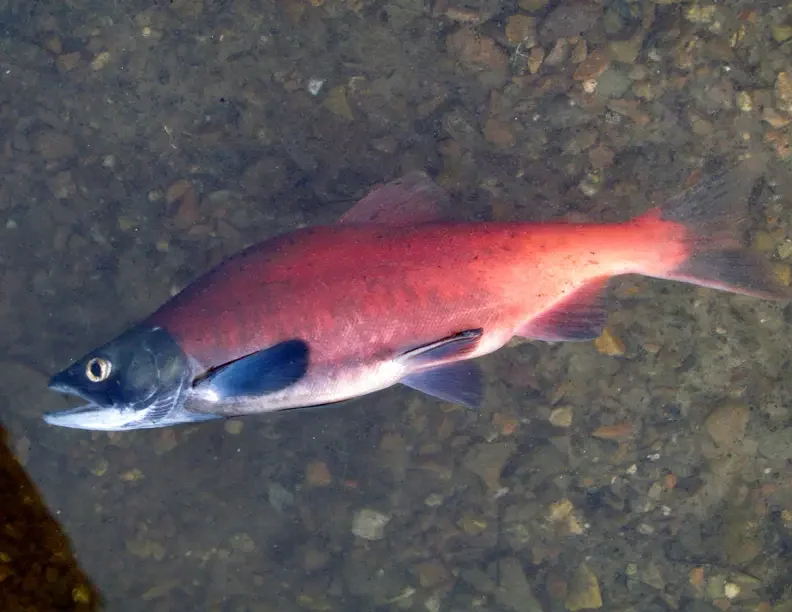
Oncorhynchus nerka |
September: Preparing for fall migration. The sockeye salmon starts returning to rivers.
Best small spoons and spinners for clear water?

- Why it works: This lightweight spoon imitates smaller baitfish with its compact size and delicate action. Its bright finishes like silver or gold work well in clear waters.
2. *Blue Fox Vibrax Jr.
- Why it works: Known for its vibrating action, this miniature spoon produces a realistic wobble even at slow retrieves. The chrome finish is particularly effective when visibility is high.
3. Ted Smith Tiny Torpedo
- Why it works: These tiny torpedoes come in sizes as small as #00, making them ideal for finicky sockeye. Their flashy patterns attract attention without being overly aggressive.
4. Daiwa Magnum Lite
- Why it works: Designed for light tackle, this spoon features a slender profile and subtle glitter finishes that blend into clear water environments.
5. Luhr Jensen Krocodile
- Why it works: A classic choice among anglers, the Krocodile's intricate shape mimics injured baitfish. The smaller sizes (#0 - #2) are perfect for clear - water sockeye.
- Why it works: Available in sizes down to #0, the Mepps Comet offers a gentle spin and reflective blade colors such as silver and copper that work well in clear conditions.
2. Panther Martin
- Why it works: The Panther Martin’s compact design and vibrant color options make it an excellent choice for targeting picky sockeye. Try the smaller models (#00 - #1).
3. Rooster Tail
- Why it works: Although larger versions can be too flashy, the smallest Rooster Tails (#00 - #1) provide just enough vibration and subtle movement to entice sockeye in clear water.
4. Black Fly
- Why it works: Black flies feature a simple but highly effective design with minimal flash. They’re great for low - light or extremely clear conditions where fish are more cautious.
5. Bomber Fat Free Shad
- Why it works: While technically a plug, the Fat Free Shad has spinner - like characteristics. Its small size and sleek profile make it suitable for clear - water presentations.
- Retrieve Speed: Use slower retrieves to match the behavior of wounded or struggling baitfish.
- Depth Control: Focus on retrieving your lure within the upper 10 - 20 feet of the water column where sockeye often feed.
- Experimentation: Rotate between different sizes and styles throughout the day to find what the fish prefer.
By selecting from these small spoons and spinners tailored for clear water, you’ll increase your chances of success when targeting selective sockeye salmon.
Most effective fly patterns for nerka: shrimp imitations?

When targeting sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), shrimp imitation flies are indeed highly effective due to the species' natural diet preferences and feeding behavior during spawning runs. Here are some of the most effective fly patterns that mimic shrimp or krill, which can be very productive when fishing for selective sockeye:
Top Fly Patterns for Sockeye Salmon 1. Muddler Minnow
- A classic pattern with a bulbous head that mimics the shape and movement of small crustaceans like shrimp. Effective in both stillwater and moving water conditions.
2. Marabou Shrimp
- This fly features marabou feathers that create an impression of shrimp - like appendages. The flashy materials attract attention underwater.
3. Zonker Shrimp
- Zonkers have long, flowing hair that resemble shrimp legs and antennae. They come in various colors but pink, orange, and white are particularly effective.
4. Flashback Woolly Bugger
- Although not specifically designed as a shrimp imitation, its profile and flashing materials make it attractive to sockeye, especially when fished slowly through deep pools.
5. Prawn Flies
- These flies feature rubber legs and bodies in bright colors such as red, orange, and pink. They closely replicate the appearance and action of actual prawns.
6. Clouser Minnow
- Another versatile pattern that works well as a shrimp imitation. Its weighted design allows for deeper presentations, making it ideal for fishing in faster currents.
- A classic pattern with a bulbous head that mimics the shape and movement of small crustaceans like shrimp. Effective in both stillwater and moving water conditions.
2. Marabou Shrimp
- This fly features marabou feathers that create an impression of shrimp - like appendages. The flashy materials attract attention underwater.
3. Zonker Shrimp
- Zonkers have long, flowing hair that resemble shrimp legs and antennae. They come in various colors but pink, orange, and white are particularly effective.
4. Flashback Woolly Bugger
- Although not specifically designed as a shrimp imitation, its profile and flashing materials make it attractive to sockeye, especially when fished slowly through deep pools.
5. Prawn Flies
- These flies feature rubber legs and bodies in bright colors such as red, orange, and pink. They closely replicate the appearance and action of actual prawns.
6. Clouser Minnow
- Another versatile pattern that works well as a shrimp imitation. Its weighted design allows for deeper presentations, making it ideal for fishing in faster currents.
Effective natural baits: shrimp, roe, maggots?

Effective natural baits for selective sockeye include shrimp, which closely mimic their natural prey, and roe, which replicates the visual and olfactory cues of eggs. Maggots can also be effective but are less commonly associated with sockeye diets compared to shrimp and roe.
How to choose small wobblers for nerka?

To select the best small wobblers for targeting sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), consider these key factors:
1. Size and Weight - Small wobblers are typically between 4 - 7 cm long.
- Lightweight wobblers work well in shallow or slow - moving waters, while slightly heavier ones can be more effective in deeper or faster currents.
2. Color and Pattern - Bright colors like red, orange, pink, and silver often attract sockeye due to their natural prey preferences.
- Natural patterns that mimic smaller fish or shrimp - like movements tend to work better during clear water conditions.
- In murky or stained water, opt for brighter, high - contrast colors such as chartreuse, yellow, or black.
3. Action Type - Wobbling action mimicking injured or struggling baitfish is crucial for attracting sockeye.
- Choose lures with a moderate to wide wobble that create an erratic swimming motion.
4. Depth Range - Ensure your chosen wobbler can reach the depth where sockeye are actively feeding. This usually ranges from 2 - 6 meters depending on location and season.
5. Line and Tackle Considerations - Use light to medium - action rods paired with appropriate line weights (typically 8 - 12 lb test).
- Leader material should match the size of the wobbler to avoid spooking skittish fish.
Final Recommendation: For optimal results when fishing for sockeye using small wobblers, try models known for their realistic movement and bright color schemes, such as:
- Mepps Comet (in sizes around 4 - 6 cm)
- Rapala X - Rap Minnow (sizes 4 - 7 cm)
- Vibrax Shad Rap (light - weight versions)
These lures combine attractive profiles, effective actions, and versatile color options to increase your chances of success.
- Lightweight wobblers work well in shallow or slow - moving waters, while slightly heavier ones can be more effective in deeper or faster currents.
- Natural patterns that mimic smaller fish or shrimp - like movements tend to work better during clear water conditions.
- In murky or stained water, opt for brighter, high - contrast colors such as chartreuse, yellow, or black.
- Choose lures with a moderate to wide wobble that create an erratic swimming motion.
- Leader material should match the size of the wobbler to avoid spooking skittish fish.
- Mepps Comet (in sizes around 4 - 6 cm)
- Rapala X - Rap Minnow (sizes 4 - 7 cm)
- Vibrax Shad Rap (light - weight versions)
These lures combine attractive profiles, effective actions, and versatile color options to increase your chances of success.
How to use subtle scents for cautious nerka?

- Avoid overly pungent or artificial smells which might spook the fish.
- Incorporate subtle scent - enhancing finishes or coatings specifically designed for sockeye.
- These subtle fragrances mimic natural food sources without overwhelming the fish's senses.
- Apply only a very thin layer - just enough to tease their interest but not overpower them.
- This targeted approach allows you to control exactly where the scent is released.
- In murky or stained waters, slightly stronger scents may work better due to reduced visibility.
By carefully selecting and applying subtle scents, you’ll create a presentation that appeals to cautious sockeye while maintaining their comfort level.
How to work flies with precise control?

To effectively fish for Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye Salmon) in clear water using flies and achieve precise fly control, consider the following techniques:
1. Leader Selection - Use a tapered leader of 7 - 9 feet in length with a terminal tippet size between 4X and 6X depending on water clarity and fish wariness.
- Fluorocarbon leaders are ideal as they have low visibility underwater due to their refractive index similar to that of water.
2. Fly Presentation - Dead Drift: This is crucial when fishing clear waters. Let's the fly drift naturally without any added movement. Simulate an injured or drifting prey by mending your line upstream to correct drag.
- Twitching/Strip Retrieves: For more aggressive presentations, use short twitches or slow strips to mimic wounded baitfish. Keep retrieves slow and subtle, matching the natural movements of local aquatic insects or small fish.
3. Fly Depth Control - Adjust depth by varying retrieve speed and tension on the line. Slow retrieves allow the fly to sink deeper into the water column while faster retrieves keep it closer to the surface.
- Consider adding weighted flies or split shot if necessary to reach target depths.
4. Casting Accuracy - Practice casting accuracy to place the fly precisely where you want it. Make sure the fly lands softly and naturally to avoid spooking wary fish.
- Pay attention to wind direction and current flow to ensure accurate placement.
5. Line Management - Maintain tight line control during the retrieve to feel even the slightest strike. Use rod tip sensitivity to detect subtle takes.
- When mending, do so gently to minimize disturbance on the water’s surface.
6. Fly Choices - Choose patterns that imitate local food sources such as Emergers, Nymphs, Wet Flies, Streamers, or Egg Patterns based on the time of year and the salmon's feeding habits.
- Popular patterns include Woolly Buggers, Marabou Leeches, and egg - simulating flies like Glo - Bugs or San Juan Worms.
7. Reading the Water - Observe the water carefully to identify likely holding spots such as pools, riffles, drop - offs, and structure areas where sockeye might be resting or feeding.
- Fish slower currents first before moving to faster - moving sections.
By mastering these techniques, you'll improve your ability to present flies with precision and increase your chances of catching Oncorhynchus nerka in clear - water environments.
- Fluorocarbon leaders are ideal as they have low visibility underwater due to their refractive index similar to that of water.
- Twitching/Strip Retrieves: For more aggressive presentations, use short twitches or slow strips to mimic wounded baitfish. Keep retrieves slow and subtle, matching the natural movements of local aquatic insects or small fish.
- Consider adding weighted flies or split shot if necessary to reach target depths.
- Pay attention to wind direction and current flow to ensure accurate placement.
- When mending, do so gently to minimize disturbance on the water’s surface.
- Popular patterns include Woolly Buggers, Marabou Leeches, and egg - simulating flies like Glo - Bugs or San Juan Worms.
- Fish slower currents first before moving to faster - moving sections.
By mastering these techniques, you'll improve your ability to present flies with precision and increase your chances of catching Oncorhynchus nerka in clear - water environments.
How to present lures subtly to wary nerka?

To effectively and subtly present lures to wary Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye salmon or Нерка), especially in clear water conditions where fish are more cautious, anglers should focus on the following techniques:
1. Use Natural - Looking Lures - Choose lures that mimic natural prey such as small baitfish, leeches, or insects. Smaller, streamlined profiles often work best.
- Opt for subtle colors like silver, gold, olive, and iridescent hues that blend well with clear waters.
2. Slow and Steady Retrieve - Use a slow, steady retrieve mimicking injured or struggling prey. This can entice wary fish into striking without alarming them.
- Occasionally pause your retrieve to let the lure sink slightly before resuming movement.
3. Minimize Line Visibility - Use clear or low - visibility fluorocarbon leader material to reduce line visibility in clear water.
- Keep line tension minimal to avoid creating unnecessary bubbles or disturbances.
4. Subtle Vibrations - Utilize lures that produce gentle vibrations rather than loud or erratic movements. Subtle vibration can attract attention without spooking fish.
- Consider using smaller spinnerbaits, inline spinners, or soft plastics rigged weedless.
5. Fish from a Distance - Position yourself further away from likely holding areas of нерка when casting. This reduces the likelihood of disturbing their environment.
- Employ longer rods (7 - 9 feet) to achieve better casting distance and accuracy.
6. Polarized Sunglasses - Wear polarized sunglasses to spot fish more easily underwater. This allows you to adjust your presentation based on their behavior.
7. Avoid Excessive Noise - Be mindful of noise levels while fishing. Avoid splashing or making sudden noises near the water's surface.
By combining these techniques, you can increase your chances of successfully presenting lures to wary нерка in clear water environments.
- Opt for subtle colors like silver, gold, olive, and iridescent hues that blend well with clear waters.
- Occasionally pause your retrieve to let the lure sink slightly before resuming movement.
- Keep line tension minimal to avoid creating unnecessary bubbles or disturbances.
- Consider using smaller spinnerbaits, inline spinners, or soft plastics rigged weedless.
- Employ longer rods (7 - 9 feet) to achieve better casting distance and accuracy.
By combining these techniques, you can increase your chances of successfully presenting lures to wary нерка in clear water environments.
Drift fishing techniques in crystal clear rivers?

- Lures/Bait: Opt for small, natural - looking lures like spoons, jigs, or flies mimicking local aquatic insects or baitfish. Small egg patterns can also be very productive.
- Leader Material: Fluorocarbon leaders (4 - 6 lb) provide excellent invisibility in clear water.
- Use Natural Cover: Fish near structure such as rocks, logs, or pools where fish may hold.
- Stay Low & Stealthy: In clear waters, visibility is high, so avoid casting shadows directly over fish. Stay low and move slowly to minimize disturbance.
- Vary Depth: Experiment with different depths by adjusting the weight of your lure or using split shot weights to reach specific zones where fish might be holding.
- Natural Action: Allow the lure to drift naturally through riffles and pools without excessive movement.
- Observe Surface Activity: Watch for signs of rising fish or subtle surface disturbances that indicate feeding activity.
- High Water Clarity: When visibility exceeds 10 feet, stick with smaller, more realistic presentations.
By employing these drift - fishing techniques, you’ll significantly increase your chances of successfully catching Oncorhynchus nerka in clear - water environments.
Float fishing tactics for selective biters?

- Reel: Opt for a small - to - medium capacity reel spooled with 4 - 8 lb test line.
- Floats: Employ small, sensitive floats like waggler or pencil floats to minimize disturbance.
- Artificial Lures: Small jigs or flies imitating natural prey can also be effective if used subtly.
- Hook Size: Match hook size to your chosen bait; typically #6 - #10 hooks work well.
- Weight Adjustment: Experiment with different weights until you achieve a slow, steady sink rate without excessive movement.
- Slow Retrieve: Allow the float to drift naturally, occasionally giving it gentle twitches to mimic live prey movements.
- Stealth: Minimize noise and vibrations by casting upstream or sideways, avoiding direct downstream approaches.
- Light Touch: When setting the hook, do so gently but firmly to avoid startling the fish.
- Patience: Be prepared to wait longer between casts, especially during low activity periods.
By employing these tactics, you'll increase your chances of successfully catching selective Oncorhynchus nerka while maintaining their wariness and natural behavior.
How to detect ultra-sensitive nerka bites?

To effectively detect ultra - sensitive bites from Oncorhynchus nerka ( Нерка), which is a species of Pacific salmon known for its subtle and delicate feeding behavior, anglers need to focus on several key techniques that enhance their ability to sense even the slightest contact with the fish. Here are some tips specifically tailored for clear water fishing scenarios:
1. Use Light Tackle - Use light - action rods (6 - 7 foot medium - light or ultralight action) paired with thin, sensitive lines such as 4 - 8 lb test fluorocarbon. This setup allows you to feel even the most subtle movements of the fish.
2. Choose Ultra - Sensitive Reels - Opt for reels with smooth drag systems and high gear ratios to quickly respond to any bite. The sensitivity of the reel's spool will help you notice slight line movement caused by a gentle strike.
3. Pay Attention to Line Movement - In clear waters, where visibility is excellent, watch your line carefully for any unusual twitches or dips. Even if the rod tip doesn't move much, the line itself might indicate a bite.
4. Feel the Rod Tip - Hold the rod at an angle so that you're able to feel the slightest pressure changes through the rod tip. A good - quality graphite rod with a soft tip can amplify these sensations significantly.
5. Adjust Your Presentation - When targeting ultra - sensitive biters like нерка, slow down your retrieve speed. Very slow twitching or jigging motions mimic natural prey movements more accurately, increasing the likelihood of triggering a bite.
6. Observe Fish Behavior - Observe how нерка behaves near your bait or lure. If they approach but don't commit fully, try adjusting your presentation slightly - maybe change depth, color, or size - to entice them into striking.
7. Utilize Downriggers or Lead Core - To get your bait precisely at the right depth where нерка feed, consider using downriggers or lead - core line. These tools allow precise control over depth while maintaining sensitivity.
8. Tactile Alerts - Some anglers use small bobbers or float rigs that provide visual and tactile alerts when a fish gently takes the bait. This method works well in calm conditions.
By combining these techniques, you'll be better equipped to detect those elusive, ultra - sensitive bites from нерка in clear water environments.
By combining these techniques, you'll be better equipped to detect those elusive, ultra - sensitive bites from нерка in clear water environments.
Best line types for clear water conditions?

1. Flourocarbon Lines
- Why It Works: Fluorocarbon has a refractive index similar to water, making it nearly invisible underwater. It's also highly abrasion - resistant, which is beneficial when dealing with rocky or weedy bottoms.
- Recommended Brands: Seaguar InvizX, Sunline FC, Berkley Vanish
2. Ultra - low Visibility Monofilament Lines
- Why It Works: These monofilaments have been specifically designed to minimize visibility while maintaining good knot strength and flexibility.
- Recommended Brands: P - line Clear Ice, Stren Ultra Clear
3. Microfilament Braided Superlines
- Why It Works: Microfilament braids offer exceptional sensitivity and casting distance due to their thin diameter and high breaking strength. They can be used as mainlines paired with fluorocarbon leaders for added invisibility.
- Recommended Brands: PowerPro Spectra, FireLine Micro Ice
4. Hybrid Lines (Fluoro - braid)
- Why It Works: Hybrid lines combine the best features of both fluorocarbon and braided lines - high sensitivity, low visibility, and excellent castability.
- Recommended Brands: Seaguar AbrazX, Spiderwire Stealth
5. Clear Gel - spun Braided Lines
- Why It Works: While not completely invisible like fluorocarbon, gel - spun braids provide excellent casting performance and durability, especially useful when using larger lures or flies.
- Recommended Brands: Yamamoto Senshi, Power Pro Trilene XL
Reel selection: smooth drag for hard fights?

For specialized tackle targeting sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), reel selection is critical due to the species' renowned strength and aggressive fighting style. Here are key considerations when choosing a reel with a smooth drag system:
1. Smooth Drag System - A smooth drag mechanism ensures consistent tension during prolonged battles against powerful fish like sockeye. This prevents sudden jerks or snaps that can break light lines or damage gear.
- Look for reels with sealed drag systems to prevent water intrusion, which could compromise performance.
2. Line Capacity - Match your reel's line capacity to the expected size of sockeye you’ll be fishing. For most sockeye anglers, a medium - sized spinning or baitcasting reel capable of holding 150 - 200 yards (137 - 183 meters) of 10 - 15 lb test monofilament or fluorocarbon works well.
3. Sturdy Construction - Opt for reels made from durable materials such as aluminum or graphite to handle the rigors of sockeye fishing without excessive weight.
- Ensure the reel has a robust frame and spool to resist bending under pressure.
4. Retrieval Ratio - Choose a reel with an appropriate retrieve ratio depending on your fishing technique. Spinning reels typically have lower retrieve ratios (like 4.6:1) for slower but smoother retrieves, while baitcasters may offer higher ratios (up to 7:1) for faster retrieval.
Recommended Models Some top choices include:
- Shimano Calcutta Conquest Series
- Daiwa Saltist
- Abu Garcia Revo SX
These models feature smooth drags, reliable construction, and sufficient line capacity for effective sockeye salmon fishing.
- Look for reels with sealed drag systems to prevent water intrusion, which could compromise performance.
- Ensure the reel has a robust frame and spool to resist bending under pressure.
- Shimano Calcutta Conquest Series
- Daiwa Saltist
- Abu Garcia Revo SX
These models feature smooth drags, reliable construction, and sufficient line capacity for effective sockeye salmon fishing.
Terminal tackle: small hooks and light leaders?

Yes, when targeting sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), anglers often use specialized terminal tackle that includes smaller hooks and lighter leaders to increase their chances of success. Here’s why this setup is effective:
1. Smaller Hooks:
Sockeye have relatively small mouths compared to other Pacific salmon species like chinook or coho. Smaller hooks (typically sizes #4 to #8) allow the bait or lure to be more easily ingested by the fish, leading to better hook - up rates.
2. Light Leaders:
Lighter leaders (often fluorocarbon or monofilament, ranging from 6 - 15 lb test) are less visible to the fish and reduce spooking. Sockeye can be particularly wary of heavy tackle, especially in clear waters. Lighter leaders also provide a more natural presentation of the bait or lure.
By using these techniques, anglers can improve their ability to catch sockeye while maintaining a stealthy approach that mimics natural prey movements.
1. Smaller Hooks:
Sockeye have relatively small mouths compared to other Pacific salmon species like chinook or coho. Smaller hooks (typically sizes #4 to #8) allow the bait or lure to be more easily ingested by the fish, leading to better hook - up rates.
2. Light Leaders:
Lighter leaders (often fluorocarbon or monofilament, ranging from 6 - 15 lb test) are less visible to the fish and reduce spooking. Sockeye can be particularly wary of heavy tackle, especially in clear waters. Lighter leaders also provide a more natural presentation of the bait or lure.
By using these techniques, anglers can improve their ability to catch sockeye while maintaining a stealthy approach that mimics natural prey movements.
Choosing rod action for sensitive nerka bites?

To choose the right rod action for sensitive sockeye (Oncorhynchus nerka) bites, consider these key factors:
1. Sensitivity - Look for a rod with a fast or moderate - fast action to provide good sensitivity and allow you to feel even subtle bites from cautious sockeye.
- A light - action rod may be too soft to detect delicate strikes effectively.
2. Lightweight Construction - Choose rods made of lightweight materials like graphite or carbon fiber to reduce fatigue during long fishing sessions while maintaining responsiveness.
3. Length Considerations - For sockeye, an ideal length is typically between 7'6" and 9'.
- Shorter rods are great for close - quarter casting and maneuverability, while longer ones offer better casting distance and leverage when fighting fish.
4. Line Weight and Fishing Conditions - Match your rod's line weight rating to the type of tackle you're using (light spinning or baitcasting setups).
- If targeting sockeye in clear water where they can be spooky, opt for lighter line weights (4 - 8 lb test).
5. Action Specificity - Fast - action rods bend mostly at the tip, providing excellent sensitivity but less cushioning power.
- Moderate - fast actions flex more through the upper third of the blank, offering a balance between sensitivity and power.
Recommended Rods for Sockeye - Fast - action rods: St Croix Avid or Sage Zee series.
- Moderate - fast action rods: Shimano Chronarch or G. Loomis IMX series.
- A light - action rod may be too soft to detect delicate strikes effectively.
- Shorter rods are great for close - quarter casting and maneuverability, while longer ones offer better casting distance and leverage when fighting fish.
- If targeting sockeye in clear water where they can be spooky, opt for lighter line weights (4 - 8 lb test).
- Moderate - fast actions flex more through the upper third of the blank, offering a balance between sensitivity and power.
- Moderate - fast action rods: Shimano Chronarch or G. Loomis IMX series.
Fly fishing gear for selective nerka?

To effectively target sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) with fly fishing tackle, anglers typically need specialized equipment that matches the size and behavior of this species. Here are some key recommendations for selecting appropriate gear:
Rods & Reels - Rod: A medium to medium - heavy action rod between 9' - 10' is ideal. For smaller rivers or streams, a lighter - action rod around 8' - 9' can work well.
- Example: Sage One Fly Rod, Orvis Helios 3D, Redington Striper.
- Reel: Use a large arbor reel to handle strong runs and provide smooth line retrieval.
- Example: Scott Fly Reels, Scientific Angler, Abel Reels.
Lines & Leaders - Fly Line: Weight forward floating lines in weights #7 - #9 are commonly used.
- Example: Rio Gold, Airflo Super Duplex, Scientific Angler Saltwater Shooting Head.
- Leaders: A tapered leader around 8 - 10 feet long with a 15 - 20 lb tippet is recommended.
- Example: Scientific Angler Trout Leader Systems, Orvis Power Flex Fluorocarbon.
Flies Sockeye prefer flies that mimic their natural prey, such as baitfish and aquatic insects. Common patterns include:
- Streamers: Woolly Buggers, Clouser Minnows, Muddler Minnows, Zonkers.
- Nymphs: Prince Nymphs, Hare's Ear Nymphs, Pheasant Tail Nymphs.
- Dry Flies: Stimulators, Elk Hair Caddis, Humpies.
Accessories - Backing: Strong backing (200 yards minimum) rated at least 40 lbs test.
- Tippets: High - quality fluorocarbon leaders like Seaguar or Maxima.
- Strike Indicators: Optional but useful when fishing nymphs or emergers.
By carefully matching your tackle to these specifications, you’ll be better equipped to catch sockeye salmon using fly - fishing techniques.
- Example: Sage One Fly Rod, Orvis Helios 3D, Redington Striper.
- Reel: Use a large arbor reel to handle strong runs and provide smooth line retrieval.
- Example: Scott Fly Reels, Scientific Angler, Abel Reels.
- Example: Rio Gold, Airflo Super Duplex, Scientific Angler Saltwater Shooting Head.
- Leaders: A tapered leader around 8 - 10 feet long with a 15 - 20 lb tippet is recommended.
- Example: Scientific Angler Trout Leader Systems, Orvis Power Flex Fluorocarbon.
- Streamers: Woolly Buggers, Clouser Minnows, Muddler Minnows, Zonkers.
- Nymphs: Prince Nymphs, Hare's Ear Nymphs, Pheasant Tail Nymphs.
- Dry Flies: Stimulators, Elk Hair Caddis, Humpies.
- Tippets: High - quality fluorocarbon leaders like Seaguar or Maxima.
- Strike Indicators: Optional but useful when fishing nymphs or emergers.
By carefully matching your tackle to these specifications, you’ll be better equipped to catch sockeye salmon using fly - fishing techniques.
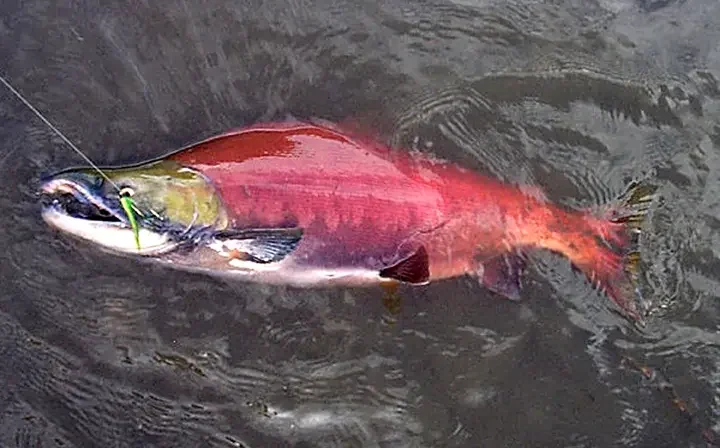
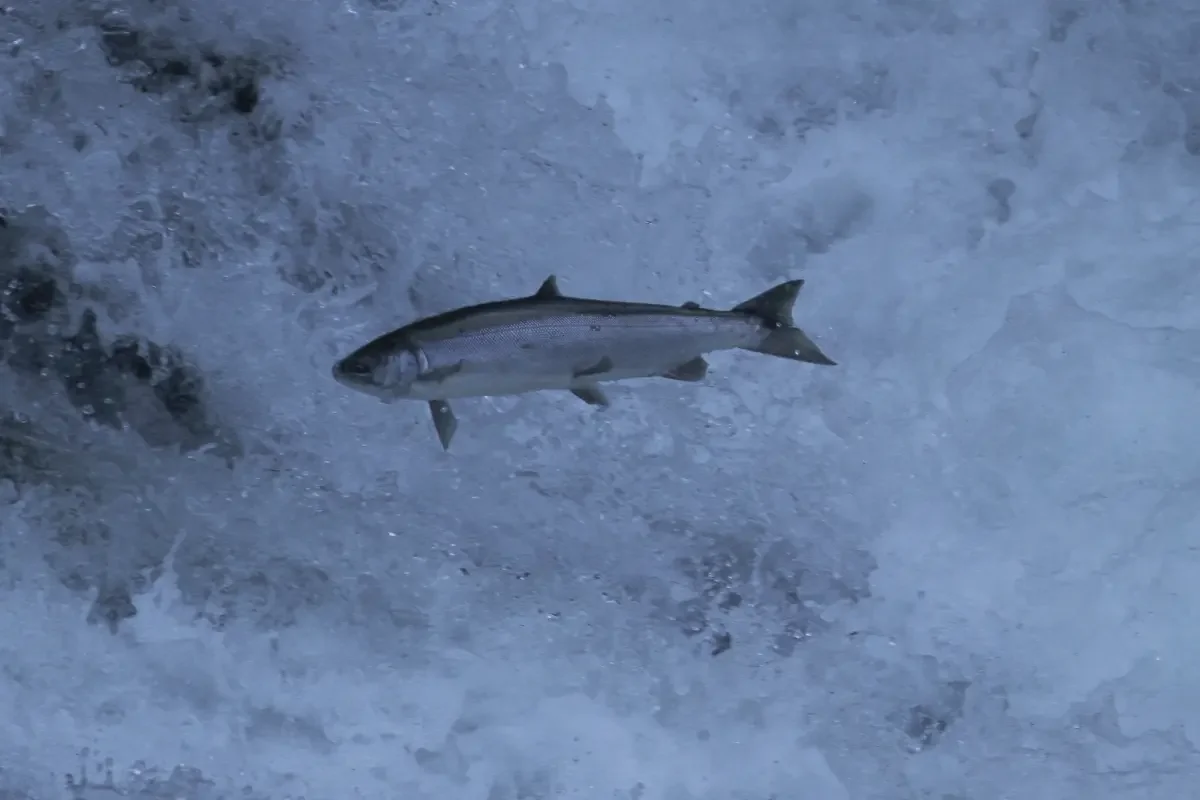
How to handle nerka's acrobatic jumps?

To effectively manage the acrobatic jumping behavior of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), consider these strategies based on their unique behaviors and fighting style:
1. Use a Strong Line and Sturdy Rod - Why it works: Sockeye are known for their powerful runs and sudden bursts of energy. A strong line (minimum 8 - 12 lb test) and a stout rod with medium - heavy action can help control their explosive movements without breaking gear.
2. Keep Tight Contact - Why it works: When a sockeye makes an acrobatic jump, it's often trying to throw off the hook or break free. Keeping constant tension on the line reduces its ability to shake loose.
3. Let the Fish Run Initially - Why it works: Allowing the fish to make initial runs helps tire it out. While they may still jump, their energy will be more evenly distributed over time rather than all at once.
4. Reel Quickly During Jumps - Why it works: As soon as you feel the fish begin to rise, reel quickly to maintain pressure. This prevents them from gaining altitude and reduces the risk of losing contact during the leap.
5. Position Yourself Downstream - Why it works: Standing slightly downstream allows you to use the current to your advantage, helping to slow down the fish’s movement and making it easier to manage their leaps.
6. Avoid Overpowering the Fish - Why it works: Overpowering a sockeye too early can cause it to panic and make even more dramatic jumps. Instead, apply steady pressure while keeping the rod tip low to guide the fish toward exhaustion gradually.
By combining these techniques, anglers can better handle the dynamic and unpredictable nature of sockeye salmon's acrobatics, leading to successful landings while minimizing stress on both the fish and equipment.
By combining these techniques, anglers can better handle the dynamic and unpredictable nature of sockeye salmon's acrobatics, leading to successful landings while minimizing stress on both the fish and equipment.
Understanding nerka's selective feeding behavior?

In freshwater environments, juveniles primarily feed on zooplankton such as copepods and amphipods. This diet provides essential nutrients needed for growth and development.
- Adult Phase:
Once they migrate to the ocean, adults transition to a carnivorous diet, preying predominantly on small fish, squid, and crustaceans like krill. The high - energy content of these prey items supports their energy - intensive spawning migrations later in life.
- Juveniles tend to remain closer to the surface where zooplankton are abundant.
- Adults often forage at deeper depths, particularly during daylight hours, when their preferred prey species are more active.
- During the day, adults typically rest near the seabed while avoiding predators.
- At night, they ascend to mid - water layers to actively hunt for prey.
- Their eyes have evolved to enhance vision in low - light conditions, enabling effective nocturnal hunting.
- Their migration routes and feeding habits also influence nutrient cycling between marine and freshwater environments.
In summary, the selective feeding behavior of Oncorhynchus nerka is characterized by dietary specialization based on life stages, habitat segregation, time - of - day activity patterns, and physical adaptations. These factors collectively ensure optimal nutrition acquisition throughout their lifecycle.
Fighting techniques for powerful sustained runs?

Taxon: Oncorhynchus nerka
(Sockeye Salmon)
Unique Behavior and Fighting Style The sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) is renowned for its impressive endurance during spawning migrations, particularly its ability to perform powerful, sustained runs over long distances against strong currents and rapids. Here are the key fighting techniques that enable this behavior:
1. Streamlined Body Shape:
The body of a sockeye salmon is laterally compressed with a torpedo - like shape, reducing drag and allowing efficient movement through water.
2. Powerful Muscles:
Their large red muscles (often referred to as "steak muscle") provide exceptional strength and endurance, enabling them to maintain high speeds over extended periods.
3. Tail Power:
A deep forked tail provides significant thrust, propelling the fish forward with each stroke while minimizing energy loss.
4. Adaptive Respiratory System:
Highly efficient gills allow sockeye salmon to extract oxygen effectively from flowing water, even when swimming upstream against strong currents.
5. Navigation Skills:
They use their lateral line system to sense changes in water pressure and direction, helping them navigate efficiently around obstacles and find optimal routes.
6. Energy Conservation Strategies:
During migration, they alternate between active bursts of speed and slower, more relaxed swimming phases to conserve energy.
7. Aggression and Territoriality:
When competing for spawning grounds, male sockeye salmon exhibit aggressive behaviors such as charging, biting, and displaying bright colors to deter rivals.
These combined physical adaptations and behavioral strategies make sockeye salmon one of nature's most formidable migratory fighters.
(Sockeye Salmon)
1. Streamlined Body Shape:
The body of a sockeye salmon is laterally compressed with a torpedo - like shape, reducing drag and allowing efficient movement through water.
2. Powerful Muscles:
Their large red muscles (often referred to as "steak muscle") provide exceptional strength and endurance, enabling them to maintain high speeds over extended periods.
3. Tail Power:
A deep forked tail provides significant thrust, propelling the fish forward with each stroke while minimizing energy loss.
4. Adaptive Respiratory System:
Highly efficient gills allow sockeye salmon to extract oxygen effectively from flowing water, even when swimming upstream against strong currents.
5. Navigation Skills:
They use their lateral line system to sense changes in water pressure and direction, helping them navigate efficiently around obstacles and find optimal routes.
6. Energy Conservation Strategies:
During migration, they alternate between active bursts of speed and slower, more relaxed swimming phases to conserve energy.
7. Aggression and Territoriality:
When competing for spawning grounds, male sockeye salmon exhibit aggressive behaviors such as charging, biting, and displaying bright colors to deter rivals.
These combined physical adaptations and behavioral strategies make sockeye salmon one of nature's most formidable migratory fighters.
Playing tactics in strong lake currents?

Taxon: Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye Salmon)
Category: Unique Behavior & Fighting Style
Specific Query: What are the playing or movement tactics of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) when navigating and interacting within strong lake currents?
Answer Sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) exhibit unique behavioral adaptations for navigating strong lake currents during their life cycle stages, particularly during migration to spawning grounds. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their movement strategies and interactions:
1. Energy Efficiency through Current Utilization:
Sockeye salmon often orient themselves to swim diagonally across current flows rather than directly against them. This diagonal swimming tactic minimizes energy expenditure while still progressing toward their destination.
2. Formation Swimming ("Schooling"):
By schooling together, individuals can reduce drag and share the burden of navigating strong currents. Leading fish create vortices that trailing fish use to conserve energy.
3. Bursts of Speed and Strategic Positioning:
When encountering particularly strong sections of current, sockeye salmon may employ short bursts of speed to overcome obstacles or move into calmer waters temporarily. They also position themselves in areas with eddies or slower - moving water where possible.
4. Avoidance of Predators via Group Dynamics:
In addition to navigational efficiency, group behavior helps deter predators such as piscivorous birds and larger fish by creating confusion and reducing individual vulnerability.
5. Surface and Depth Adjustments:
Depending on the strength and direction of the current, sockeye salmon adjust their depth within the water column. Surface swimming might be used to take advantage of wind - driven waves, while deeper swimming can exploit more stable flow conditions.
6. Physical Adaptations Supporting Movement Tactics:
Their streamlined bodies and powerful tail muscles allow efficient propulsion even in turbulent environments. Additionally, their lateral line system enhances their ability to sense changes in water pressure and current dynamics.
These behaviors highlight how sockeye salmon have evolved sophisticated strategies to navigate challenging aquatic environments effectively.
Category: Unique Behavior & Fighting Style
Specific Query: What are the playing or movement tactics of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) when navigating and interacting within strong lake currents?
1. Energy Efficiency through Current Utilization:
Sockeye salmon often orient themselves to swim diagonally across current flows rather than directly against them. This diagonal swimming tactic minimizes energy expenditure while still progressing toward their destination.
2. Formation Swimming ("Schooling"):
By schooling together, individuals can reduce drag and share the burden of navigating strong currents. Leading fish create vortices that trailing fish use to conserve energy.
3. Bursts of Speed and Strategic Positioning:
When encountering particularly strong sections of current, sockeye salmon may employ short bursts of speed to overcome obstacles or move into calmer waters temporarily. They also position themselves in areas with eddies or slower - moving water where possible.
4. Avoidance of Predators via Group Dynamics:
In addition to navigational efficiency, group behavior helps deter predators such as piscivorous birds and larger fish by creating confusion and reducing individual vulnerability.
5. Surface and Depth Adjustments:
Depending on the strength and direction of the current, sockeye salmon adjust their depth within the water column. Surface swimming might be used to take advantage of wind - driven waves, while deeper swimming can exploit more stable flow conditions.
6. Physical Adaptations Supporting Movement Tactics:
Their streamlined bodies and powerful tail muscles allow efficient propulsion even in turbulent environments. Additionally, their lateral line system enhances their ability to sense changes in water pressure and current dynamics.
These behaviors highlight how sockeye salmon have evolved sophisticated strategies to navigate challenging aquatic environments effectively.
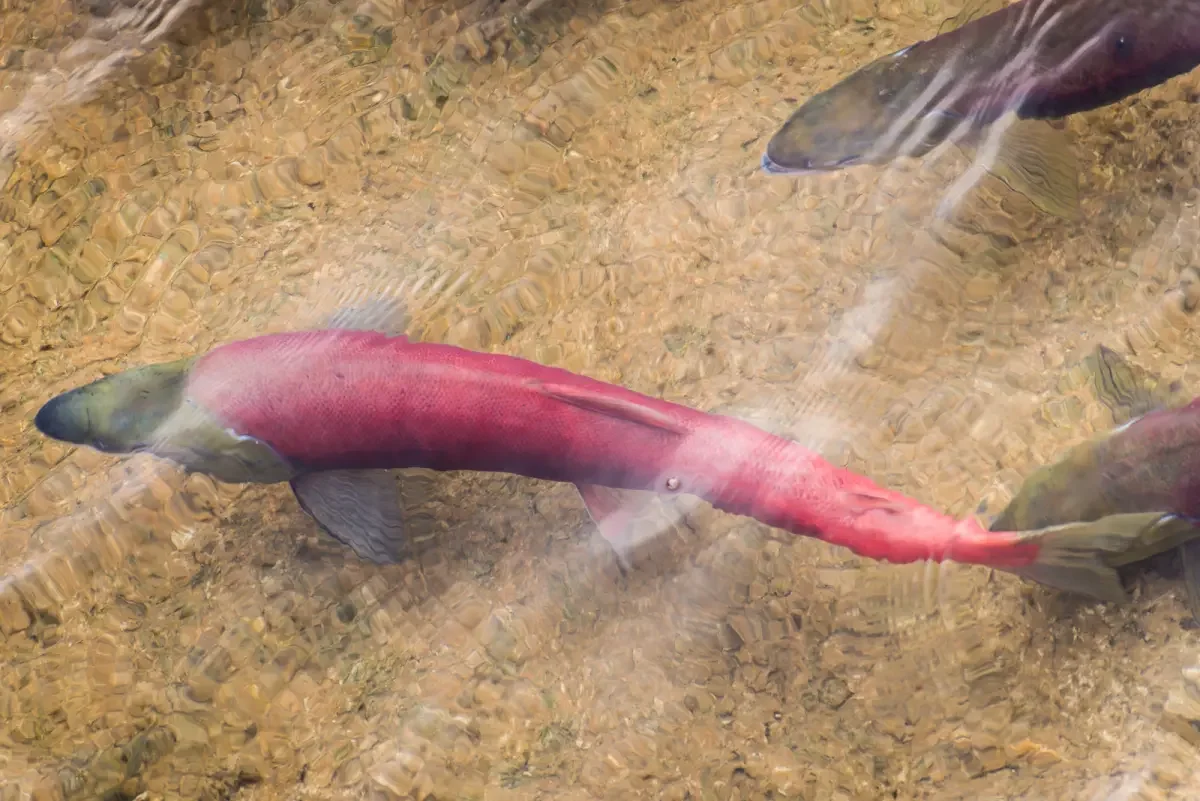
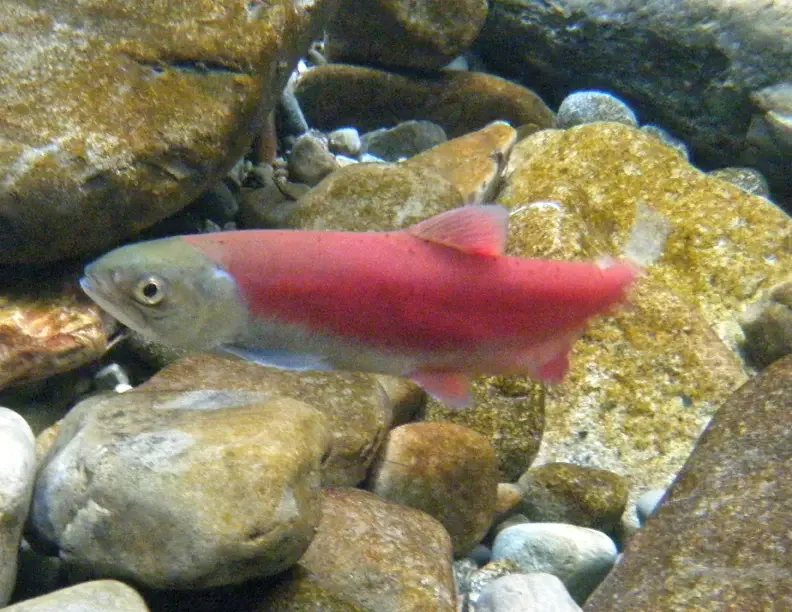
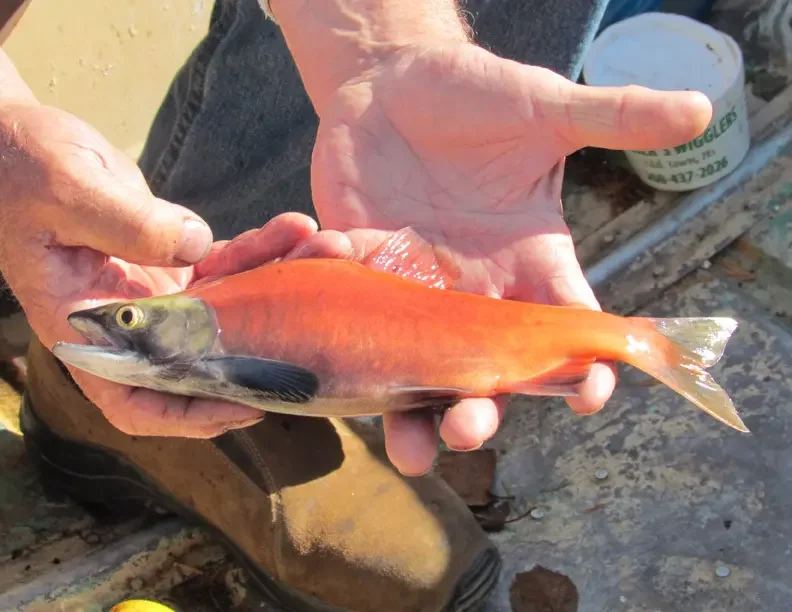
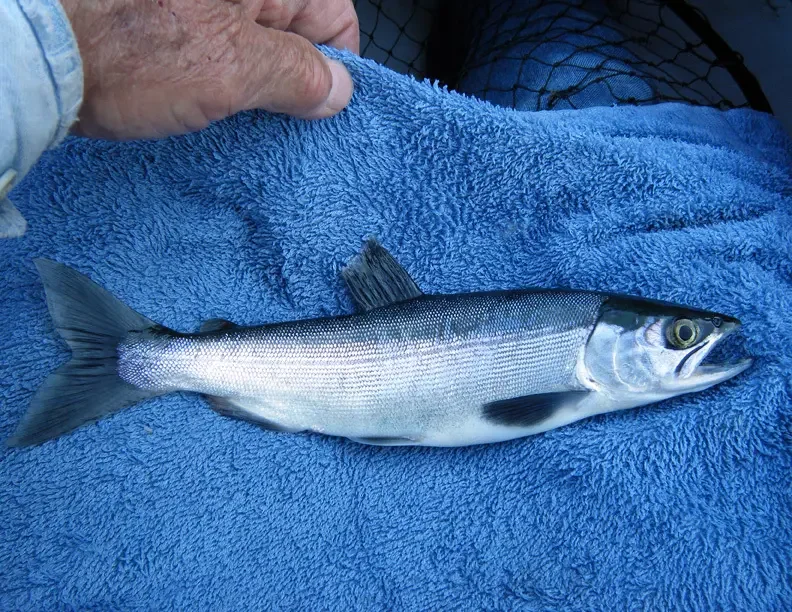
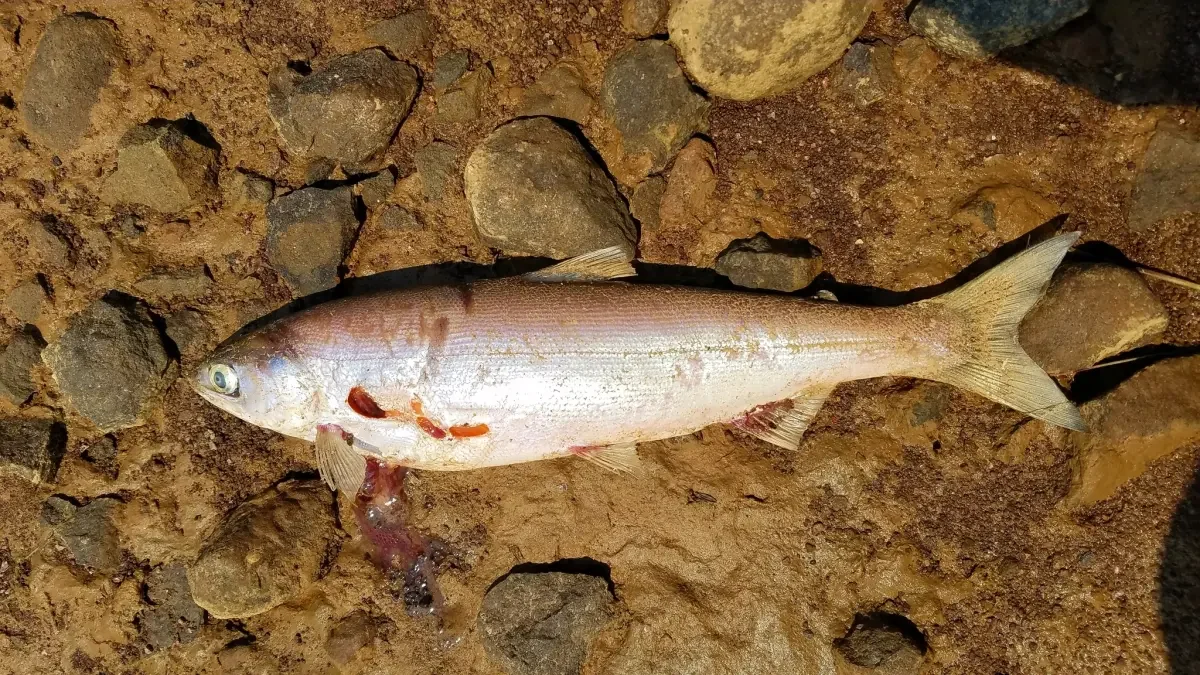
How to identify pre-spawn vs. spawning nerka?

To identify pre - spawn versus spawning phases of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), consider the following key behavioral and physical differences:
Pre - Spawn Phase (Mature but not yet Spawning) 1. Physical Appearance
- Body coloration is still predominantly silver with a few hints of red or pink on sides and belly.
- Males may show slight changes in body shape, such as a slightly humped back, but this is less pronounced than during full spawning.
2. Behavioral Traits
- Fish are actively migrating upstream toward their spawning grounds.
- They exhibit relatively low aggression levels compared to fully matured spawners.
- Females begin selecting nesting sites, but actual nest - building behavior hasn't started yet.
Spawning Phase (Fully Maturing for Reproduction) 1. Physical Appearance
- Bright red or orange body coloration, especially noticeable on males.
- Males develop a hooked upper jaw (kype) and large teeth.
- Both sexes have darker heads and bellies, often with dark vertical bars.
- Skin texture becomes rougher due to increased mucus production.
2. Behavioral Traits
- Highly aggressive interactions between individuals, particularly among males competing for mates.
- Active nest - building by females using their tails to dig redds (nests).
- Pair bonding between male and female fish occurs near selected nesting areas.
- Posture and movements become more erratic and territorial, with frequent displays of dominance.
By observing these distinct behaviors and physical characteristics, you can accurately distinguish between pre - spawn and spawning stages of sockeye salmon.
- Body coloration is still predominantly silver with a few hints of red or pink on sides and belly.
- Males may show slight changes in body shape, such as a slightly humped back, but this is less pronounced than during full spawning.
2. Behavioral Traits
- Fish are actively migrating upstream toward their spawning grounds.
- They exhibit relatively low aggression levels compared to fully matured spawners.
- Females begin selecting nesting sites, but actual nest - building behavior hasn't started yet.
- Bright red or orange body coloration, especially noticeable on males.
- Males develop a hooked upper jaw (kype) and large teeth.
- Both sexes have darker heads and bellies, often with dark vertical bars.
- Skin texture becomes rougher due to increased mucus production.
2. Behavioral Traits
- Highly aggressive interactions between individuals, particularly among males competing for mates.
- Active nest - building by females using their tails to dig redds (nests).
- Pair bonding between male and female fish occurs near selected nesting areas.
- Posture and movements become more erratic and territorial, with frequent displays of dominance.
By observing these distinct behaviors and physical characteristics, you can accurately distinguish between pre - spawn and spawning stages of sockeye salmon.
When do specific nerka runs occur in different systems?

Taxon Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye salmon) has distinct spawning runs that vary depending on the geographic location and river system. Here are general patterns for sockeye runs across several notable regions in Russia and North America:
Russia 1. Kamchatka Peninsula
- Kamchatka River System: Spawning runs typically begin in late June through early September, peaking around July - August.
- Ozernaya River: Mid - July to mid - September.
2. Bering Sea Region
- Anadyr River: Late June to August.
- Koryaksky Peninsula rivers: Early July to mid - August.
North America 1. Alaska
- Bristol Bay region (Nushagak, Kvichak Rivers): Major runs from late May to early October, with peak activity in June - July.
- Copper River: June to early August.
- Kenai River: Main run occurs from late May to mid - June.
2. British Columbia, Canada
- Fraser River: Multiple runs, but primary ones span May to October, with major peaks in June - August.
- Chilko Lake (Chilcotin River): Mid - May to early July.
3. Washington State, USA
- Columbia River: Runs generally happen between April and November, with significant spawning periods in June - September.
4. Idaho, USA
- Salmon River: Typically from late May to early September, with a main peak in June - July.
These timings can fluctuate slightly year - to - year based on environmental conditions such as water temperature, flow rates, and ocean conditions.
- Kamchatka River System: Spawning runs typically begin in late June through early September, peaking around July - August.
- Ozernaya River: Mid - July to mid - September.
2. Bering Sea Region
- Anadyr River: Late June to August.
- Koryaksky Peninsula rivers: Early July to mid - August.
- Bristol Bay region (Nushagak, Kvichak Rivers): Major runs from late May to early October, with peak activity in June - July.
- Copper River: June to early August.
- Kenai River: Main run occurs from late May to mid - June.
2. British Columbia, Canada
- Fraser River: Multiple runs, but primary ones span May to October, with major peaks in June - August.
- Chilko Lake (Chilcotin River): Mid - May to early July.
3. Washington State, USA
- Columbia River: Runs generally happen between April and November, with significant spawning periods in June - September.
4. Idaho, USA
- Salmon River: Typically from late May to early September, with a main peak in June - July.
These timings can fluctuate slightly year - to - year based on environmental conditions such as water temperature, flow rates, and ocean conditions.
What water temperature triggers nerka migration?

The migration of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) is primarily triggered by a combination of environmental cues, including water temperature. A critical factor for initiating their upstream migration from marine environments to freshwater spawning grounds is when the water temperature drops to approximately 10 - 14°C (50 - 57°F).
This range signals favorable conditions for their journey and subsequent reproduction. Sockeye salmon are particularly sensitive to temperature changes during different stages of their life cycle, with cooler temperatures prompting them to move into rivers toward their natal spawning sites.
This range signals favorable conditions for their journey and subsequent reproduction. Sockeye salmon are particularly sensitive to temperature changes during different stages of their life cycle, with cooler temperatures prompting them to move into rivers toward their natal spawning sites.
How to predict exact timing of nerka arrivals?

Predicting the precise timing and run patterns of Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye salmon or Нерка) requires a combination of historical data analysis, environmental monitoring, and advanced modeling techniques. Here are key factors and steps that can help improve predictions for their arrival times:
1. Historical Data Analysis - Analyze past migration records from local fisheries management agencies or research institutions.
- Identify trends such as average arrival dates, peak migration periods, and variability between years.
2. Environmental Monitoring - Monitor water temperature, flow rates, and other hydrological conditions known to influence migration behavior.
- Track oceanographic conditions like sea surface temperatures and currents, which impact offshore feeding grounds.
3. Biological Indicators - Observe spawning readiness indicators in returning adults, such as changes in body coloration, fat content, and gonadal development.
- Use genetic markers to track specific populations and understand their unique life history traits.
4. Advanced Modeling Techniques - Develop predictive models using machine learning algorithms trained on historical datasets.
- Incorporate real - time environmental data into these models to refine predictions dynamically.
5. Citizen Science and Community Engagement - Engage local communities and anglers in reporting sightings and catch data through apps or online platforms.
- Aggregate this information with scientific observations to create more comprehensive datasets.
By combining these approaches, you can enhance the accuracy of predicting when sockeye salmon will arrive at their spawning grounds. This is crucial not only for fishery management but also for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these iconic species.
- Identify trends such as average arrival dates, peak migration periods, and variability between years.
- Track oceanographic conditions like sea surface temperatures and currents, which impact offshore feeding grounds.
- Use genetic markers to track specific populations and understand their unique life history traits.
- Incorporate real - time environmental data into these models to refine predictions dynamically.
- Aggregate this information with scientific observations to create more comprehensive datasets.
By combining these approaches, you can enhance the accuracy of predicting when sockeye salmon will arrive at their spawning grounds. This is crucial not only for fishery management but also for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these iconic species.
How to find early-run "ocean bright" nerka?

To locate and target early - run "ocean bright" sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka), anglers need a combination of knowledge about the species' life cycle, migration patterns, environmental conditions, and specific fishing techniques. Here are some key strategies for finding these fish during their early runs:
1. Understand Life Cycle Phases - Early - Run Definition: Early - run sockeye typically enter freshwater earlier than main - stock populations, often showing less coloration (retaining silver scales and brighter appearance).
- Migration Timing: Research historical data on local river systems where early - run sockeye are known to spawn. Early run timing can vary by region but generally occurs from late spring through mid - summer.
2. Identify Habitat Preferences - Preferred Waters: Ocean - bright sockeye prefer cooler water temperatures (around 54 - 60°F/12 - 16°C) with high oxygen levels. They tend to be found in deeper pools or areas with strong currents that mimic ocean - like environments.
- River Sections: Focus on sections of rivers near estuaries or upstream tributaries where fish first enter freshwater. These areas may have more consistent cool water flows.
3. Use Environmental Indicators - Water Temperature Monitoring: Track daily water temperature fluctuations using gauges or online resources. Cold fronts or rain events can trigger early migrations.
- Tidal Influences: For coastal rivers, pay attention to tidal cycles. Higher tides can push fish further upriver.
4. Fish Behavior Observations - Surface Activity: Look for signs of feeding activity such as birds diving into the water or splashing at the surface.
- Fish Movement Patterns: Early - run sockeye may school together in groups, making them easier to spot when they move en masse.
5. Effective Fishing Techniques - Lures and Baits: Use lures like spoons, plugs, or jigs that imitate small baitfish. Smaller sizes (size #0 - #4) work well. Natural baits like herring or shrimp can also attract these fish.
- Depth Control: Fish at various depths depending on current conditions. Early - run sockeye might suspend in mid - depths rather than hugging the bottom.
- Fly Fishing: If fly - fishing, use streamers or egg patterns. Retrieve them slowly with pauses to mimic natural prey movements.
6. Local Knowledge and Regulations - Consult Local Experts: Talk to experienced guides, tackle shop owners, or fellow anglers who know the local waters and fish behavior.
- Check Regulations: Ensure you understand any size limits, bag limits, or restricted fishing periods for early - run sockeye.
By combining these insights - understanding the biology and habits of early - run sockeye, monitoring environmental cues, and employing effective fishing tactics - you’ll significantly improve your chances of successfully targeting this elusive and prized species.
- Migration Timing: Research historical data on local river systems where early - run sockeye are known to spawn. Early run timing can vary by region but generally occurs from late spring through mid - summer.
- River Sections: Focus on sections of rivers near estuaries or upstream tributaries where fish first enter freshwater. These areas may have more consistent cool water flows.
- Tidal Influences: For coastal rivers, pay attention to tidal cycles. Higher tides can push fish further upriver.
- Fish Movement Patterns: Early - run sockeye may school together in groups, making them easier to spot when they move en masse.
- Depth Control: Fish at various depths depending on current conditions. Early - run sockeye might suspend in mid - depths rather than hugging the bottom.
- Fly Fishing: If fly - fishing, use streamers or egg patterns. Retrieve them slowly with pauses to mimic natural prey movements.
- Check Regulations: Ensure you understand any size limits, bag limits, or restricted fishing periods for early - run sockeye.
By combining these insights - understanding the biology and habits of early - run sockeye, monitoring environmental cues, and employing effective fishing tactics - you’ll significantly improve your chances of successfully targeting this elusive and prized species.
Fishing strategies for short peak run windows?

- Monitor migration patterns and environmental cues such as water temperature, river flow rates, and moon phases to predict precise timing.
- Use historical data from previous years to identify typical peak run periods.
2. Target Prime Locations:
- Focus on areas with optimal habitat conditions like deep pools, slow - moving sections, or gravel beds where spawning occurs.
- Identify confluences of tributaries or narrow passages that concentrate fish movement.
3. Selective Gear Usage:
- Employ selective fishing gear such as single hooks, barbless hooks, or catch - and - release techniques to minimize impact during the critical spawning period.
- Avoid gillnets or seines if possible, especially in sensitive habitats.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
- Adhere strictly to local regulations regarding bag limits, size restrictions, and closed seasons to ensure sustainable populations.
- Collaborate with fisheries management agencies to understand any temporary closures or restricted zones.
5. Weather Adaptation:
- Be prepared for variable weather conditions by having appropriate clothing and equipment.
- Consider fishing early mornings or late evenings when temperatures are cooler and fish activity peaks.
6. Conservation Awareness:
- Educate fellow anglers about the importance of conserving sockeye salmon stocks during their short but crucial reproductive runs.
- Support conservation efforts through organizations working towards habitat restoration and population monitoring.
By combining these strategies, you can maximize your chances of successful fishing while minimizing negative impacts on this iconic species.
How to find fresh "blueback" nerka before turning red?

To locate and catch fresh blueback sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) before they turn red, you need to understand their migration patterns, habitat preferences, and seasonal behavior. Here are some strategies for finding them effectively in lake and river systems:
1. Timing of Migration - Bluebacks typically enter rivers earlier than other sockeye populations during the summer months (June - August).
- Monitor local fisheries reports or talk with experienced anglers to determine peak migration periods in your area.
2. Preferred Habitat - Fresh bluebacks prefer cooler water temperatures (around 50°F/10°C), so look for deeper, colder sections of lakes and rivers.
- They often swim along drop - offs, deep channels, and areas with strong currents where oxygen levels are high.
3. River Entrance Points - Focus on river mouths and estuaries where bluebacks first enter from the ocean.
- Use polarized sunglasses to spot schools swimming upstream near the surface.
4. Tidal Influences - If fishing in coastal rivers, pay attention to tidal cycles. Bluebacks tend to move more actively during incoming tides when the current helps push them upriver.
5. Fishing Techniques - Troll slowly using downriggers or planers to reach depths where bluebacks school.
- Use brightly colored lures like spoons, plugs, or flies that mimic small baitfish.
- Fish around structures such as submerged logs, rocks, or islands where bluebacks may rest while moving upstream.
- Monitor local fisheries reports or talk with experienced anglers to determine peak migration periods in your area.
- They often swim along drop - offs, deep channels, and areas with strong currents where oxygen levels are high.
- Use polarized sunglasses to spot schools swimming upstream near the surface.
- Use brightly colored lures like spoons, plugs, or flies that mimic small baitfish.
- Fish around structures such as submerged logs, rocks, or islands where bluebacks may rest while moving upstream.
How to locate nerka migration routes in lake-connected rivers?

To effectively locate the migration routes of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) in lake - connected river systems, you can follow these strategies and steps:
1. Historical Data Analysis - Review historical records, fisheries data, and scientific studies that document previous sockeye migrations in the area.
- Identify key spawning grounds and known migration corridors from past observations.
2. Field Surveys and Monitoring - Conduct field surveys during peak migration periods (typically spring through summer).
- Use mark - recapture techniques or tagging programs to track individual fish movements.
- Install sonar equipment or underwater cameras at strategic points along suspected migration paths.
3. Habitat Assessment - Evaluate the physical characteristics of potential migration routes such as water depth, flow rate, temperature, and substrate type.
- Focus on areas with suitable conditions for spawning (gravel beds, clean flowing water), which are often key indicators of migration pathways.
4. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Mapping - Utilize GIS technology to map and analyze environmental variables like elevation, slope, and hydrological connectivity between lakes and rivers.
- Overlap this information with habitat suitability models to predict likely migration routes.
5. Community Knowledge - Engage local communities, fishermen, and Indigenous knowledge holders who may have traditional ecological knowledge about sockeye migration patterns.
- Collaborate with them to identify critical habitats and historical migration hotspots.
6. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Sampling - Collect water samples at various locations within the river system and use eDNA analysis to detect the presence of sockeye salmon genetic material.
- This method helps confirm the presence of migrating fish without physically capturing them.
By combining these approaches, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of sockeye salmon migration routes in lake - connected rivers, enabling effective conservation and management efforts.
- Identify key spawning grounds and known migration corridors from past observations.
- Use mark - recapture techniques or tagging programs to track individual fish movements.
- Install sonar equipment or underwater cameras at strategic points along suspected migration paths.
- Focus on areas with suitable conditions for spawning (gravel beds, clean flowing water), which are often key indicators of migration pathways.
- Overlap this information with habitat suitability models to predict likely migration routes.
- Collaborate with them to identify critical habitats and historical migration hotspots.
- This method helps confirm the presence of migrating fish without physically capturing them.
By combining these approaches, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of sockeye salmon migration routes in lake - connected rivers, enabling effective conservation and management efforts.
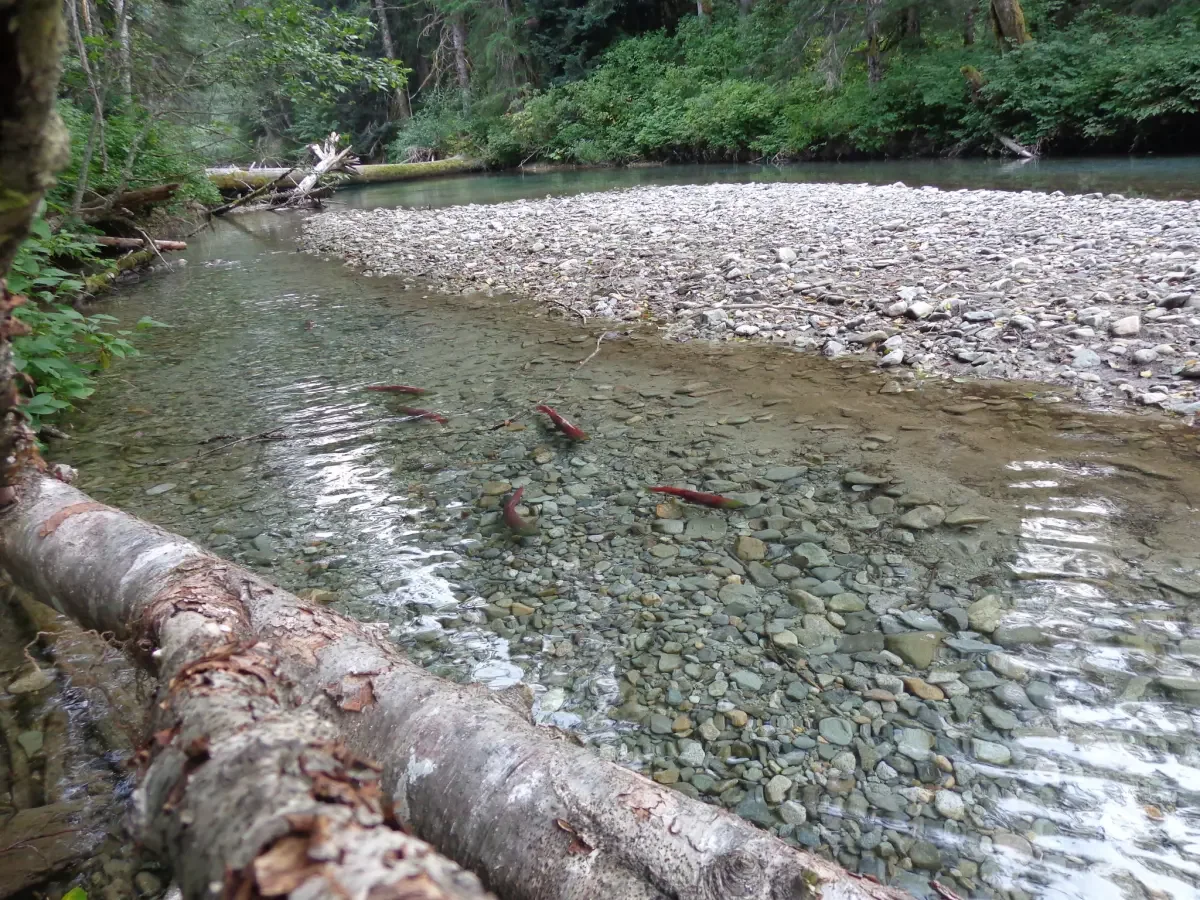
Tactics for finding nerka in lake outlets and inlets?

To find Oncorhynchus nerka (Nerka or sockeye salmon) in lake outlets and inlets, consider the following strategies based on their natural behavior, habitat preferences, and seasonal migration patterns:
1. Seasonal Timing - Nerka typically enter lakes during spring through early summer to spawn in rivers and streams connected to the lake. Pay attention to peak spawning periods specific to your region.
2. Water Temperature Monitoring - Nerka prefer cooler water temperatures (around 9 - 15°C). Use temperature probes or fishfinders to locate areas with suitable temperatures near inlets/outlets.
3. Current Flow Analysis - Look for areas where currents converge or diverge at river mouths or lake outlets. These locations often attract feeding fish due to increased food availability.
4. Structure and Cover - Focus on areas with underwater structures such as rocks, submerged logs, or weed beds that provide cover from predators and current flows.
5. Baitfish Presence - Observe bird activity and baitfish schools around inlet/outlet zones. Baitfish presence is a strong indicator of potential nerka aggregation.
6. Tidal Influence - If fishing near tidal waters, time your efforts with incoming tides when nerka are more likely to move into shallower areas.
7. Visual Scanning - Use polarized sunglasses to spot fish rising to feed or moving in schools just below the surface.
8. Fishing Gear Selection - Utilize downrigger weights, lead - core line, or diving plugs to reach deeper layers where nerka may be holding.
By combining these tactics, you can effectively target nerka in both lake outlet and inlet environments.
By combining these tactics, you can effectively target nerka in both lake outlet and inlet environments.
How to locate nerka holding in deep lake areas before river entry?

To effectively locate Oncorhynchus nerka ( Нерка or sockeye salmon) holding in deep lake areas prior to their migration into rivers, the following strategies can be employed:
1. Acoustic and Hydroacoustic Monitoring - Use sonar equipment such as split - beam echosounders to detect fish schools at various depths within lakes.
- Multi - frequency hydroacoustic surveys help identify fish aggregations based on their acoustic signatures.
2. Temperature and Oxygen Profiles - Monitor water temperature and dissolved oxygen levels across different depths since sockeye prefer cooler waters with higher oxygen content during pre - spawning periods.
- Deploy thermistor chains or CTD (conductivity - temperature - depth) probes to map thermal layers where fish may aggregate.
3. Fish Behavioral Observations - Observe surface behaviors like feeding activity or splashing which might indicate deeper aggregation zones.
- Track bird activity over water bodies; birds often congregate above schools of fish.
4. GPS Tagging and Tracking - Attach satellite or acoustic tags to individual fish to track their movements and depth preferences.
- This method provides detailed information about specific locations and depths used by нерка.
5. Underwater Video Surveys - Conduct underwater video surveys using remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) equipped with cameras to visually inspect potential holding areas.
6. Biological Sampling - Collect biological samples from different depths to analyze species composition and abundance.
- Fish traps or seines set at varying depths can capture individuals for identification and population estimation.
7. Historical Data Analysis - Review historical data on нерка spawning migrations and known holding areas to predict likely locations.
- Compare current environmental conditions with past years' patterns to refine predictions.
By combining these methods, researchers and managers can accurately pinpoint нерка holding areas in deep lake systems before they enter rivers for spawning.
- Multi - frequency hydroacoustic surveys help identify fish aggregations based on their acoustic signatures.
- Deploy thermistor chains or CTD (conductivity - temperature - depth) probes to map thermal layers where fish may aggregate.
- Track bird activity over water bodies; birds often congregate above schools of fish.
- This method provides detailed information about specific locations and depths used by нерка.
- Fish traps or seines set at varying depths can capture individuals for identification and population estimation.
- Compare current environmental conditions with past years' patterns to refine predictions.
By combining these methods, researchers and managers can accurately pinpoint нерка holding areas in deep lake systems before they enter rivers for spawning.
Reading water clarity for optimal nerka fishing?

To successfully fish for Oncorhynchus nerka (Sockeye salmon or Нерка), understanding the lake and river system's water clarity is crucial because it directly affects where these fish will be found and how they behave. Here are some key strategies based on water clarity:
1. Clear Water Conditions - Behavior: In clear waters, sockeye tend to move deeper into the water column to avoid predators and seek cooler temperatures.
- Fishing Strategy: Use brightly colored lures or flies that mimic small baitfish. These colors stand out well in clear water. Deep - diving plugs, spoons, or jigs can be effective when fished at depths of 20 - 40 feet.
- Tactics: Focus on drop - offs, underwater structure like submerged islands, and areas with current breaks.
2. Moderate Clarity - Behavior: Fish may still remain somewhat deep but might also come closer to the surface depending on light penetration and food availability.
- Fishing Strategy: Try using intermediate - colored lures (silvers, pinks, or chartreuse) that balance visibility with natural camouflage. Sparkle patterns often work well here as they reflect light effectively.
- Tactics: Target areas near shorelines, weed beds, and shallow flats during low - light conditions such as dawn or dusk.
3. Cloudy/Turbid Water - Behavior: When water clarity drops due to sediment runoff, algae blooms, or other factors, sockeye often move closer to the surface to feed more efficiently.
- Fishing Strategy: Opt for darker, contrasting colors like black, purple, or dark greens. These lure types help fish locate prey in murky environments. Lures with flashy finishes or glow - in - the - dark properties can also attract attention.
- Tactics: Look for feeding activity near the surface, especially around shallow shoals, eddies, and inlets. Use slower retrieves to simulate injured or struggling baitfish.
General Tips Across All Conditions: - Seasonal Variation: Pay close attention to migration timing and spawning cycles. Sockeye typically enter rivers during late spring through summer, with peak runs varying by region.
- Water Temperature: Sockeyes prefer cooler water temperatures between 50°F and 60°F. Monitor temperature changes within different layers of the water column.
- Weather Patterns: Windy days can stir up sediments, changing water clarity quickly. Adjust your approach accordingly.
By carefully observing water clarity and adapting your techniques, you’ll significantly improve your chances of catching this elusive species.
- Fishing Strategy: Use brightly colored lures or flies that mimic small baitfish. These colors stand out well in clear water. Deep - diving plugs, spoons, or jigs can be effective when fished at depths of 20 - 40 feet.
- Tactics: Focus on drop - offs, underwater structure like submerged islands, and areas with current breaks.
- Fishing Strategy: Try using intermediate - colored lures (silvers, pinks, or chartreuse) that balance visibility with natural camouflage. Sparkle patterns often work well here as they reflect light effectively.
- Tactics: Target areas near shorelines, weed beds, and shallow flats during low - light conditions such as dawn or dusk.
- Fishing Strategy: Opt for darker, contrasting colors like black, purple, or dark greens. These lure types help fish locate prey in murky environments. Lures with flashy finishes or glow - in - the - dark properties can also attract attention.
- Tactics: Look for feeding activity near the surface, especially around shallow shoals, eddies, and inlets. Use slower retrieves to simulate injured or struggling baitfish.
- Water Temperature: Sockeyes prefer cooler water temperatures between 50°F and 60°F. Monitor temperature changes within different layers of the water column.
- Weather Patterns: Windy days can stir up sediments, changing water clarity quickly. Adjust your approach accordingly.
By carefully observing water clarity and adapting your techniques, you’ll significantly improve your chances of catching this elusive species.
How to distinguish nerka from other salmon species?

- Body shape: They have a slender, torpedo - shaped body with a relatively small head compared to their length.
- Adult females: Also turn red but lack the pronounced humpback seen in males.
- Juveniles and non - spawning adults: Typically silver on the sides and belly, with dark blue - green backs.
- Tail fin: Has a distinct forked appearance with radiating rays that form a V - shape when viewed from behind.
- Anal fin: Smaller than the dorsal fin, positioned closer to the tail.
- Pectoral fins: Usually clear or translucent without spots.
- Teeth: Generally absent in most populations except for a few specialized forms where teeth may be present.
| - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - | - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - |
| Body color | Bright red during spawning | Dark gray/olive - brown | Metallic blue/green |
| Head | Greenish - blue | Black spots above lateral line | Black spots below lateral line |
| Tail pattern | Forked tail | Large black spots on tail | No large spots |
| Scales | Small | Larger | Medium |
| Jaw | Hooked in males | Straight | Hooked in both sexes |
| Pectoral fins | Clear, no spots | Spotted | Clear, no spots |
| Habitat preference | Deep lakes | Rivers, estuaries | Coastal waters, rivers |
1. Sustainable Fishing Practices: Ensuring fishing quotas do not exceed sustainable levels to prevent overfishing.
2. Habitat Protection: Preserving critical habitats such as spawning grounds and rearing lakes.
3. Biodiversity Maintenance: Protecting genetic diversity within populations by avoiding selective harvesting practices.
4. Educational Outreach: Raising awareness about the importance of conservation efforts among local communities and stakeholders.
By combining accurate identification techniques with responsible management strategies, we can ensure the continued health and viability of this iconic species.
Identifying different life stages of nerka?

- Characteristics:
- Small, round, yellowish - brown eggs about 5 - 7 mm in diameter.
- Embryos develop inside the eggs over several months before hatching.
- Characteristics:
- Transparent body with a large yolk sac.
- Dark vertical stripes on the sides.
- Remain hidden under gravel until yolk sac is absorbed.
- Characteristics:
- Bright red or orange coloration on the belly.
- Distinct dark vertical bars on the sides.
- Begins active swimming and feeding on aquatic insects and zooplankton.
- Characteristics:
- Develop prominent parr marks - dark, vertical bands alternating with lighter areas.
- Streamlined body shape suitable for navigating fast - moving waters.
- May remain in this stage for up to two years depending on environmental conditions.
- Characteristics:
- Metallic silver coloration with faint horizontal markings.
- Slender body adapted for migration.
- Undergo physiological changes to adapt to salty ocean water.
- Characteristics:
- Deep blue - green back with silvery sides.
- Large size, typically reaching lengths between 50 - 80 cm.
- Live primarily in open oceans, feeding on plankton, small fish, and squid.
- Characteristics:
- Intense red coloration, especially noticeable during spawning season.
- Humped backs and hooked jaws in males.
- Diminished physical condition due to energy expenditure during migration and reproduction.
1. Sustainable Harvesting Practices: Ensuring fishing quotas do not exceed sustainable levels while maintaining genetic diversity within populations.
2. Habitat Protection: Preserving and restoring critical habitats such as spawning grounds, rearing streams, and estuaries.
3. Climate Change Mitigation: Addressing climate impacts like warming waters and altered stream flows through adaptive management strategies.
4. Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in monitoring programs and education initiatives to foster stewardship and awareness.
By understanding these life stages and adhering to ethical practices, we can ensure the long - term survival of sockeye salmon populations.
Best practices for handling and releasing nerka?

Oncorhynchus nerka, commonly known as sockeye salmon or нерка, is a species of anadromous fish native to the North Pacific Ocean and rivers flowing into it. They are renowned for their bright red flesh and vibrant coloration during spawning.
- Keep fish wet at all times. Avoid prolonged exposure to air, which can cause stress and damage gills.
2. Handle with Care:
- Use nets with soft mesh material to avoid abrasions or scale loss.
- Handle fish gently by supporting their body weight fully, avoiding pressure on internal organs.
3. Avoid Overhandling:
- Limit the time spent out of water. For catch - and - release fishing, quickly unhook and return the fish to the water.
4. Use Barbless Hooks:
- Barbless hooks facilitate easier removal without causing additional injury.
5. Revive Before Release:
- If the fish appears lethargic after being caught, revive it by holding it upright in moving water until it regains strength and can swim away unaided.
6. Release in Shallow Water:
- Place the fish back into calm, shallow areas where it can recover more easily before swimming off.
7. Respect Spawning Seasons:
- During spawning periods, consider limiting fishing efforts to protect breeding populations.
8. Report Observations:
- Share any observations about нерка health, behavior, or unusual conditions with local wildlife agencies to support conservation efforts.
By following these best practices, anglers and researchers can help ensure the long - term survival and well - being of this iconic species.
Understanding nerka's crucial role in ecosystem?

- These predators often carry uneaten fish carcasses into nearby forests, enriching soil with marine - derived nutrients.
- This nutrient transfer supports the growth of algae and aquatic plants, which in turn feed smaller organisms like zooplankton.
- These nutrients enhance productivity in lakes, rivers, and adjacent forest soils, benefitting both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
- Commercial fishing of nerka provides economic benefits to local communities, although overfishing and habitat degradation pose serious threats to sustainable harvest levels.
In summary, understanding the ecological significance of nerka highlights the need for conservation measures aimed at preserving this iconic species and maintaining healthy, functioning ecosystems.
Ethical fishing practices for sustainable nerka populations?

- Employ gear that minimizes bycatch of juvenile or undersized fish.
- Use barbless hooks to reduce injury when releasing non - target species.
2. Implement Catch - and - Release Techniques
- Release untargeted fish promptly and carefully to maximize their survival rates.
- Handle fish gently to avoid damaging their scales, fins, or protective mucus layer.
3. Follow Strict Quotas and Seasonal Closures
- Adhere strictly to fishing quotas set by management agencies.
- Respect seasonal closures designed to protect spawning adults and juveniles during critical life stages.
4. Support Habitat Restoration Efforts
- Participate in habitat restoration projects such as reforestation, streambank stabilization, and removal of barriers like dams.
- Avoid activities that degrade spawning grounds or migration routes.
5. Support Science - Based Management Decisions
- Collaborate with scientists and resource managers to ensure data - driven decisions are made regarding population health and fishing regulations.
- Advocate for continued research into the impacts of climate change on nerka populations.
6. Embrace Certification Programs
- Seek out and support certifications like Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), which promote sustainable fishing practices.
- Purchase only sustainably sourced seafood products.
By adopting these ethical fishing practices, we can help ensure healthy, thriving populations of Oncorhynchus nerka while maintaining ecological balance within their ecosystems.
15 September 2025 Good bite
16 September 2025 Good bite
17 September 2025 Good bite
18 September 2025 The average bite
19 September 2025 Good bite
20 September 2025 Good bite
21 September 2025 Good bite
16 September 2025 Good bite
17 September 2025 Good bite
18 September 2025 The average bite
19 September 2025 Good bite
20 September 2025 Good bite
21 September 2025 Good bite
 Afghanistan
Afghanistan Aland Islands
Aland Islands Albania
Albania Algeria
Algeria American Samoa
American Samoa Andorra
Andorra Angola
Angola Anguilla
Anguilla Antarctica
Antarctica Antigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda Argentina
Argentina Armenia
Armenia Aruba
Aruba Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan Bahamas
Bahamas Bahrain
Bahrain Bangladesh
Bangladesh Barbados
Barbados Belarus
Belarus Belgium
Belgium Belize
Belize Benin
Benin Bermuda
Bermuda Bhutan
Bhutan Bolivia
Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana
Botswana Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island Brazil
Brazil British Virgin Islands
British Virgin Islands Brunei
Brunei Bulgaria
Bulgaria Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso Burundi
Burundi Cambodia
Cambodia Cameroon
Cameroon Canada
Canada Cape Verde
Cape Verde Caribbean Netherlands
Caribbean Netherlands Cayman Islands
Cayman Islands Central African Republic
Central African Republic Chad
Chad Chagos
Chagos Chile
Chile China
China Christmas Island
Christmas Island Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Cocos (Keeling) Islands Colombia
Colombia Comoros
Comoros Cook Islands
Cook Islands Costa Rica
Costa Rica Croatia
Croatia Cuba
Cuba Curaçao
Curaçao Cyprus
Cyprus Czechia
Czechia DR Congo
DR Congo Democratic People's Republic of Korea
Democratic People's Republic of Korea Denmark
Denmark Djibouti
Djibouti Dominica
Dominica Dominican Republic
Dominican Republic Ecuador
Ecuador Egypt
Egypt El Salvador
El Salvador Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea Eritrea
Eritrea Estonia
Estonia Eswatini
Eswatini Ethiopia
Ethiopia Falkland Islands
Falkland Islands Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands Fiji
Fiji Finland
Finland France
France French Guiana
French Guiana French Polynesia
French Polynesia French Southern and Antarctic Lands
French Southern and Antarctic Lands Gabon
Gabon Gambia
Gambia Georgia
Georgia Germany
Germany Ghana
Ghana Gibraltar
Gibraltar Greece
Greece Greenland
Greenland Grenada
Grenada Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe Guam
Guam Guatemala
Guatemala Guernsey
Guernsey Guinea
Guinea Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau Guyana
Guyana Haiti
Haiti Heard Island and McDonald Islands
Heard Island and McDonald Islands Honduras
Honduras Hong Kong
Hong Kong Hungary
Hungary Iceland
Iceland India
India Indonesia
Indonesia Iran
Iran Iraq
Iraq Ireland
Ireland Isle of Man
Isle of Man Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast Jamaica
Jamaica Japan
Japan Jersey
Jersey Jordan
Jordan Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan Kenya
Kenya Kiribati
Kiribati Kosovo
Kosovo Kuwait
Kuwait Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan Laos
Laos Latvia
Latvia Lebanon
Lebanon Lesotho
Lesotho Liberia
Liberia Libya
Libya Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein Lithuania
Lithuania Luxembourg
Luxembourg Macau
Macau Madagascar
Madagascar Malawi
Malawi Malaysia
Malaysia Maldives
Maldives Mali
Mali Malta
Malta Marshall Islands
Marshall Islands Martinique
Martinique Mauritania
Mauritania Mauritius
Mauritius Mayotte
Mayotte Mexico
Mexico Micronesia
Micronesia Moldova
Moldova Monaco
Monaco Mongolia
Mongolia Montenegro
Montenegro Montserrat
Montserrat Morocco
Morocco Mozambique
Mozambique Myanmar
Myanmar Namibia
Namibia Nauru
Nauru Nepal
Nepal Netherlands
Netherlands Netherlands Antilles
Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia
New Caledonia New Zealand
New Zealand Nicaragua
Nicaragua Niger
Niger Nigeria
Nigeria Niue
Niue Norfolk Island
Norfolk Island North Macedonia
North Macedonia Northern Mariana Islands
Northern Mariana Islands Norway
Norway Oman
Oman Pakistan
Pakistan Palau
Palau Palestine
Palestine Panama
Panama Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea Paraguay
Paraguay Peru
Peru Philippines
Philippines Pitcairn Islands
Pitcairn Islands Poland
Poland Portugal
Portugal Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico Qatar
Qatar Republic of the Congo
Republic of the Congo Romania
Romania Russia
Russia Rwanda
Rwanda Réunion
Réunion Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia Saint Martin
Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa
Samoa San Marino
San Marino Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia Senegal
Senegal Serbia
Serbia Serbia and Montenegro
Serbia and Montenegro Seychelles
Seychelles Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone Singapore
Singapore Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands Somalia
Somalia South Africa
South Africa South Georgia
South Georgia South Korea
South Korea South Sudan
South Sudan Spain
Spain Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Sudan
Sudan Suriname
Suriname Svalbard and Jan Mayen
Svalbard and Jan Mayen Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Syria
Syria São Tomé and Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe Taiwan
Taiwan Tajikistan
Tajikistan Tanzania
Tanzania Thailand
Thailand Timor-Leste
Timor-Leste Togo
Togo Tokelau
Tokelau Tonga
Tonga Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia
Tunisia Turkey
Turkey Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu
Tuvalu Uganda
Uganda Ukraine
Ukraine United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States United States Minor Outlying Islands
United States Minor Outlying Islands United States Virgin Islands
United States Virgin Islands Uruguay
Uruguay Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan Vanuatu
Vanuatu Vatican City
Vatican City Venezuela
Venezuela Vietnam
Vietnam Wallis and Futuna
Wallis and Futuna Western Sahara
Western Sahara Yemen
Yemen Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia Zambia
Zambia Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe